一、简介
探究pcie IP代码在uboot和kernel阶段都实现哪些功能?如何实现枚举?如何实现配置空间的配置?
二、uboot
下图是代码的主要逻辑。
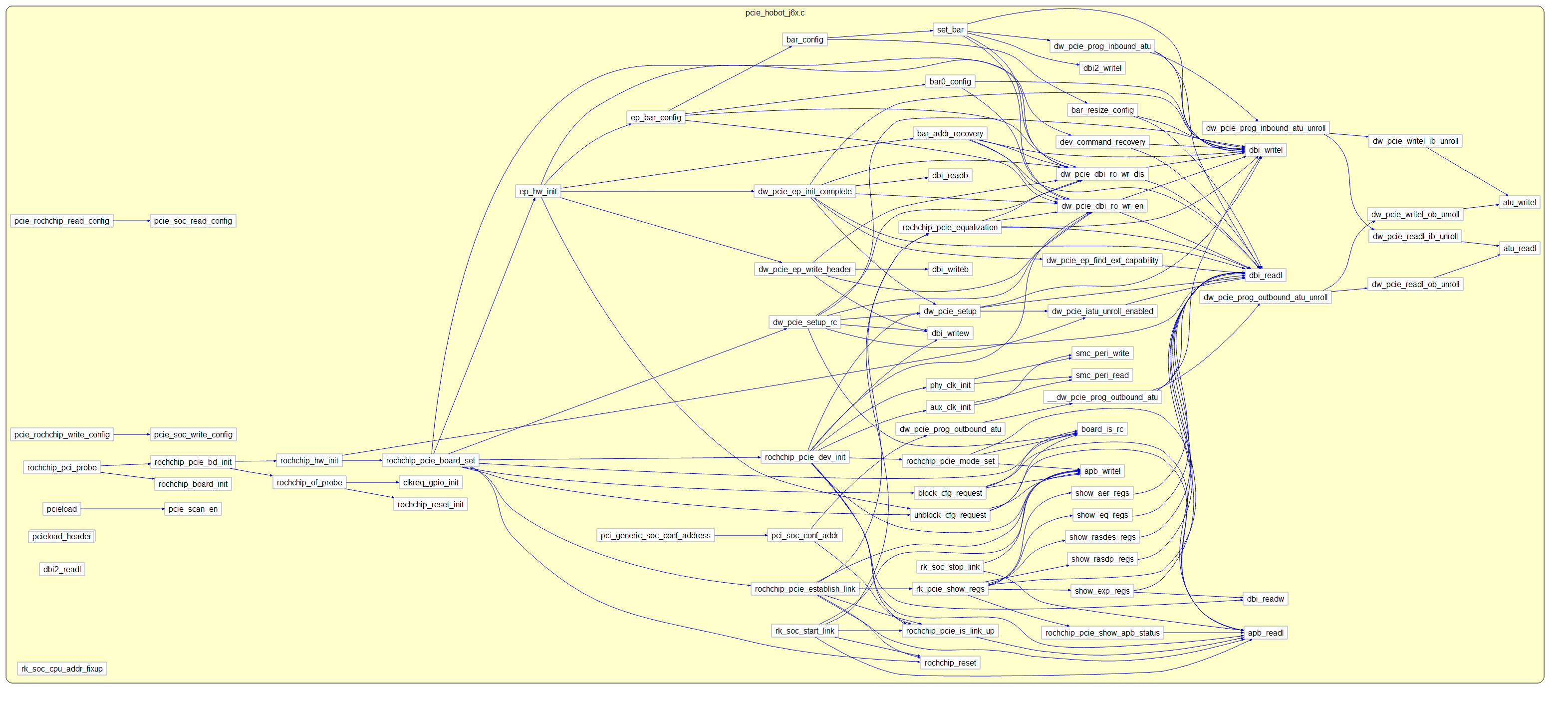 这里面有一个非常重要的pci.h,作为基础知识,需要重点学习一下。
这里面有一个非常重要的pci.h,作为基础知识,需要重点学习一下。
pci.h
/* SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-2.0+ */
/*
* (C) Copyright 2001 Sysgo Real-Time Solutions, GmbH <www.elinos.com>
* Andreas Heppel <aheppel@sysgo.de>
*
* (C) Copyright 2002
* Wolfgang Denk, DENX Software Engineering, wd@denx.de.
* Copyright (c) 2021 Maciej W. Rozycki <macro@orcam.me.uk>
*/
#ifndef _PCI_H
#define _PCI_H
#define PCI_CFG_SPACE_SIZE 256
#define PCI_CFG_SPACE_EXP_SIZE 4096
/*
* Under PCI, each device has 256 bytes of configuration address space,
* of which the first 64 bytes are standardized as follows:
*/
#define PCI_STD_HEADER_SIZEOF 64
#define PCI_VENDOR_ID 0x00 /* 16 bits */
#define PCI_DEVICE_ID 0x02 /* 16 bits */
#define PCI_COMMAND 0x04 /* 16 bits */
#define PCI_COMMAND_IO 0x1 /* Enable response in I/O space */
#define PCI_COMMAND_MEMORY 0x2 /* Enable response in Memory space */
#define PCI_COMMAND_MASTER 0x4 /* Enable bus mastering */
#define PCI_COMMAND_SPECIAL 0x8 /* Enable response to special cycles */
#define PCI_COMMAND_INVALIDATE 0x10 /* Use memory write and invalidate */
#define PCI_COMMAND_VGA_PALETTE 0x20 /* Enable palette snooping */
#define PCI_COMMAND_PARITY 0x40 /* Enable parity checking */
#define PCI_COMMAND_WAIT 0x80 /* Enable address/data stepping */
#define PCI_COMMAND_SERR 0x100 /* Enable SERR */
#define PCI_COMMAND_FAST_BACK 0x200 /* Enable back-to-back writes */
#define PCI_COMMAND_INTX_DISABLE 0x400 /* INTx Emulation Disable */
#define PCI_STATUS 0x06 /* 16 bits */
#define PCI_STATUS_CAP_LIST 0x10 /* Support Capability List */
#define PCI_STATUS_66MHZ 0x20 /* Support 66 Mhz PCI 2.1 bus */
#define PCI_STATUS_UDF 0x40 /* Support User Definable Features [obsolete] */
#define PCI_STATUS_FAST_BACK 0x80 /* Accept fast-back to back */
#define PCI_STATUS_PARITY 0x100 /* Detected parity error */
#define PCI_STATUS_DEVSEL_MASK 0x600 /* DEVSEL timing */
#define PCI_STATUS_DEVSEL_FAST 0x000
#define PCI_STATUS_DEVSEL_MEDIUM 0x200
#define PCI_STATUS_DEVSEL_SLOW 0x400
#define PCI_STATUS_SIG_TARGET_ABORT 0x800 /* Set on target abort */
#define PCI_STATUS_REC_TARGET_ABORT 0x1000 /* Master ack of " */
#define PCI_STATUS_REC_MASTER_ABORT 0x2000 /* Set on master abort */
#define PCI_STATUS_SIG_SYSTEM_ERROR 0x4000 /* Set when we drive SERR */
#define PCI_STATUS_DETECTED_PARITY 0x8000 /* Set on parity error */
#define PCI_CLASS_REVISION 0x08 /* High 24 bits are class, low 8
revision */
#define PCI_REVISION_ID 0x08 /* Revision ID */
#define PCI_CLASS_PROG 0x09 /* Reg. Level Programming Interface */
#define PCI_CLASS_DEVICE 0x0a /* Device class */
#define PCI_CLASS_CODE 0x0b /* Device class code */
#define PCI_CLASS_CODE_TOO_OLD 0x00
#define PCI_CLASS_CODE_STORAGE 0x01
#define PCI_CLASS_CODE_NETWORK 0x02
#define PCI_CLASS_CODE_DISPLAY 0x03
#define PCI_CLASS_CODE_MULTIMEDIA 0x04
#define PCI_CLASS_CODE_MEMORY 0x05
#define PCI_CLASS_CODE_BRIDGE 0x06
#define PCI_CLASS_CODE_COMM 0x07
#define PCI_CLASS_CODE_PERIPHERAL 0x08
#define PCI_CLASS_CODE_INPUT 0x09
#define PCI_CLASS_CODE_DOCKING 0x0A
#define PCI_CLASS_CODE_PROCESSOR 0x0B
#define PCI_CLASS_CODE_SERIAL 0x0C
#define PCI_CLASS_CODE_WIRELESS 0x0D
#define PCI_CLASS_CODE_I2O 0x0E
#define PCI_CLASS_CODE_SATELLITE 0x0F
#define PCI_CLASS_CODE_CRYPTO 0x10
#define PCI_CLASS_CODE_DATA 0x11
/* Base Class 0x12 - 0xFE is reserved */
#define PCI_CLASS_CODE_OTHER 0xFF
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE 0x0a /* Device sub-class code */
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_TOO_OLD_NOTVGA 0x00
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_TOO_OLD_VGA 0x01
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_STORAGE_SCSI 0x00
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_STORAGE_IDE 0x01
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_STORAGE_FLOPPY 0x02
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_STORAGE_IPIBUS 0x03
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_STORAGE_RAID 0x04
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_STORAGE_ATA 0x05
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_STORAGE_SATA 0x06
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_STORAGE_SAS 0x07
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_STORAGE_OTHER 0x80
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_NETWORK_ETHERNET 0x00
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_NETWORK_TOKENRING 0x01
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_NETWORK_FDDI 0x02
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_NETWORK_ATM 0x03
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_NETWORK_ISDN 0x04
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_NETWORK_WORLDFIP 0x05
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_NETWORK_PICMG 0x06
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_NETWORK_OTHER 0x80
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_DISPLAY_VGA 0x00
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_DISPLAY_XGA 0x01
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_DISPLAY_3D 0x02
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_DISPLAY_OTHER 0x80
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_MULTIMEDIA_VIDEO 0x00
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_MULTIMEDIA_AUDIO 0x01
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_MULTIMEDIA_PHONE 0x02
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_MULTIMEDIA_OTHER 0x80
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_MEMORY_RAM 0x00
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_MEMORY_FLASH 0x01
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_MEMORY_OTHER 0x80
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_BRIDGE_HOST 0x00
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_BRIDGE_ISA 0x01
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_BRIDGE_EISA 0x02
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_BRIDGE_MCA 0x03
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_BRIDGE_PCI 0x04
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_BRIDGE_PCMCIA 0x05
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_BRIDGE_NUBUS 0x06
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_BRIDGE_CARDBUS 0x07
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_BRIDGE_RACEWAY 0x08
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_BRIDGE_SEMI_PCI 0x09
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_BRIDGE_INFINIBAND 0x0A
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_BRIDGE_OTHER 0x80
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_COMM_SERIAL 0x00
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_COMM_PARALLEL 0x01
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_COMM_MULTIPORT 0x02
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_COMM_MODEM 0x03
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_COMM_GPIB 0x04
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_COMM_SMARTCARD 0x05
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_COMM_OTHER 0x80
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_PERIPHERAL_PIC 0x00
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_PERIPHERAL_DMA 0x01
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_PERIPHERAL_TIMER 0x02
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_PERIPHERAL_RTC 0x03
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_PERIPHERAL_HOTPLUG 0x04
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_PERIPHERAL_SD 0x05
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_PERIPHERAL_OTHER 0x80
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_INPUT_KEYBOARD 0x00
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_INPUT_DIGITIZER 0x01
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_INPUT_MOUSE 0x02
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_INPUT_SCANNER 0x03
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_INPUT_GAMEPORT 0x04
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_INPUT_OTHER 0x80
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_DOCKING_GENERIC 0x00
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_DOCKING_OTHER 0x80
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_PROCESSOR_386 0x00
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_PROCESSOR_486 0x01
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_PROCESSOR_PENTIUM 0x02
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_PROCESSOR_ALPHA 0x10
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_PROCESSOR_POWERPC 0x20
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_PROCESSOR_MIPS 0x30
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_PROCESSOR_COPROC 0x40
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_SERIAL_1394 0x00
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_SERIAL_ACCESSBUS 0x01
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_SERIAL_SSA 0x02
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_SERIAL_USB 0x03
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_SERIAL_FIBRECHAN 0x04
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_SERIAL_SMBUS 0x05
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_SERIAL_INFINIBAND 0x06
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_SERIAL_IPMI 0x07
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_SERIAL_SERCOS 0x08
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_SERIAL_CANBUS 0x09
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_WIRELESS_IRDA 0x00
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_WIRELESS_IR 0x01
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_WIRELESS_RF 0x10
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_WIRELESS_BLUETOOTH 0x11
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_WIRELESS_BROADBAND 0x12
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_WIRELESS_80211A 0x20
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_WIRELESS_80211B 0x21
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_WIRELESS_OTHER 0x80
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_I2O_V1_0 0x00
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_SATELLITE_TV 0x01
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_SATELLITE_AUDIO 0x02
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_SATELLITE_VOICE 0x03
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_SATELLITE_DATA 0x04
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_CRYPTO_NETWORK 0x00
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_CRYPTO_ENTERTAINMENT 0x10
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_CRYPTO_OTHER 0x80
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_DATA_DPIO 0x00
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_DATA_PERFCNTR 0x01
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_DATA_COMMSYNC 0x10
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_DATA_MGMT 0x20
#define PCI_CLASS_SUB_CODE_DATA_OTHER 0x80
#define PCI_CACHE_LINE_SIZE 0x0c /* 8 bits */
#define PCI_LATENCY_TIMER 0x0d /* 8 bits */
#define PCI_HEADER_TYPE 0x0e /* 8 bits */
#define PCI_HEADER_TYPE_MASK 0x7f
#define PCI_HEADER_TYPE_NORMAL 0
#define PCI_HEADER_TYPE_BRIDGE 1
#define PCI_HEADER_TYPE_CARDBUS 2
#define PCI_BIST 0x0f /* 8 bits */
#define PCI_BIST_CODE_MASK 0x0f /* Return result */
#define PCI_BIST_START 0x40 /* 1 to start BIST, 2 secs or less */
#define PCI_BIST_CAPABLE 0x80 /* 1 if BIST capable */
/*
* Base addresses specify locations in memory or I/O space.
* Decoded size can be determined by writing a value of
* 0xffffffff to the register, and reading it back. Only
* 1 bits are decoded.
*/
#define PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_0 0x10 /* 32 bits */
#define PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_1 0x14 /* 32 bits [htype 0,1 only] */
#define PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_2 0x18 /* 32 bits [htype 0 only] */
#define PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_3 0x1c /* 32 bits */
#define PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_4 0x20 /* 32 bits */
#define PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_5 0x24 /* 32 bits */
#define PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_SPACE 0x01 /* 0 = memory, 1 = I/O */
#define PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_SPACE_IO 0x01
#define PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_SPACE_MEMORY 0x00
#define PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_MEM_TYPE_MASK 0x06
#define PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_MEM_TYPE_32 0x00 /* 32 bit address */
#define PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_MEM_TYPE_1M 0x02 /* Below 1M [obsolete] */
#define PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_MEM_TYPE_64 0x04 /* 64 bit address */
#define PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_MEM_PREFETCH 0x08 /* prefetchable? */
#define PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_MEM_MASK (~0x0fULL)
#define PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_IO_MASK (~0x03ULL)
/* bit 1 is reserved if address_space = 1 */
/* Convert a regsister address (e.g. PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_1) to a bar # (e.g. 1) */
#define pci_offset_to_barnum(offset) \
(((offset) - PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_0) / sizeof(u32))
/* Header type 0 (normal devices) */
#define PCI_CARDBUS_CIS 0x28
#define PCI_SUBSYSTEM_VENDOR_ID 0x2c
#define PCI_SUBSYSTEM_ID 0x2e
#define PCI_ROM_ADDRESS 0x30 /* Bits 31..11 are address, 10..1 reserved */
#define PCI_ROM_ADDRESS_ENABLE 0x01
#define PCI_ROM_ADDRESS_MASK (~0x7ffULL)
#define PCI_CAPABILITY_LIST 0x34 /* Offset of first capability list entry */
/* 0x35-0x3b are reserved */
#define PCI_INTERRUPT_LINE 0x3c /* 8 bits */
#define PCI_INTERRUPT_PIN 0x3d /* 8 bits */
#define PCI_MIN_GNT 0x3e /* 8 bits */
#define PCI_MAX_LAT 0x3f /* 8 bits */
#define PCI_INTERRUPT_LINE_DISABLE 0xff
/* Header type 1 (PCI-to-PCI bridges) */
#define PCI_PRIMARY_BUS 0x18 /* Primary bus number */
#define PCI_SECONDARY_BUS 0x19 /* Secondary bus number */
#define PCI_SUBORDINATE_BUS 0x1a /* Highest bus number behind the bridge */
#define PCI_SEC_LATENCY_TIMER 0x1b /* Latency timer for secondary interface */
#define PCI_IO_BASE 0x1c /* I/O range behind the bridge */
#define PCI_IO_LIMIT 0x1d
#define PCI_IO_RANGE_TYPE_MASK 0x0f /* I/O bridging type */
#define PCI_IO_RANGE_TYPE_16 0x00
#define PCI_IO_RANGE_TYPE_32 0x01
#define PCI_IO_RANGE_MASK ~0x0f
#define PCI_SEC_STATUS 0x1e /* Secondary status register, only bit 14 used */
#define PCI_MEMORY_BASE 0x20 /* Memory range behind */
#define PCI_MEMORY_LIMIT 0x22
#define PCI_MEMORY_RANGE_TYPE_MASK 0x0f
#define PCI_MEMORY_RANGE_MASK ~0x0f
#define PCI_PREF_MEMORY_BASE 0x24 /* Prefetchable memory range behind */
#define PCI_PREF_MEMORY_LIMIT 0x26
#define PCI_PREF_RANGE_TYPE_MASK 0x0f
#define PCI_PREF_RANGE_TYPE_32 0x00
#define PCI_PREF_RANGE_TYPE_64 0x01
#define PCI_PREF_RANGE_MASK ~0x0f
#define PCI_PREF_BASE_UPPER32 0x28 /* Upper half of prefetchable memory range */
#define PCI_PREF_LIMIT_UPPER32 0x2c
#define PCI_IO_BASE_UPPER16 0x30 /* Upper half of I/O addresses */
#define PCI_IO_LIMIT_UPPER16 0x32
/* 0x34 same as for htype 0 */
/* 0x35-0x3b is reserved */
#define PCI_ROM_ADDRESS1 0x38 /* Same as PCI_ROM_ADDRESS, but for htype 1 */
/* 0x3c-0x3d are same as for htype 0 */
#define PCI_BRIDGE_CONTROL 0x3e
#define PCI_BRIDGE_CTL_PARITY 0x01 /* Enable parity detection on secondary interface */
#define PCI_BRIDGE_CTL_SERR 0x02 /* The same for SERR forwarding */
#define PCI_BRIDGE_CTL_NO_ISA 0x04 /* Disable bridging of ISA ports */
#define PCI_BRIDGE_CTL_VGA 0x08 /* Forward VGA addresses */
#define PCI_BRIDGE_CTL_MASTER_ABORT 0x20 /* Report master aborts */
#define PCI_BRIDGE_CTL_BUS_RESET 0x40 /* Secondary bus reset */
#define PCI_BRIDGE_CTL_FAST_BACK 0x80 /* Fast Back2Back enabled on secondary interface */
/* Header type 2 (CardBus bridges) */
#define PCI_CB_CAPABILITY_LIST 0x14
/* 0x15 reserved */
#define PCI_CB_SEC_STATUS 0x16 /* Secondary status */
#define PCI_CB_PRIMARY_BUS 0x18 /* PCI bus number */
#define PCI_CB_CARD_BUS 0x19 /* CardBus bus number */
#define PCI_CB_SUBORDINATE_BUS 0x1a /* Subordinate bus number */
#define PCI_CB_LATENCY_TIMER 0x1b /* CardBus latency timer */
#define PCI_CB_MEMORY_BASE_0 0x1c
#define PCI_CB_MEMORY_LIMIT_0 0x20
#define PCI_CB_MEMORY_BASE_1 0x24
#define PCI_CB_MEMORY_LIMIT_1 0x28
#define PCI_CB_IO_BASE_0 0x2c
#define PCI_CB_IO_BASE_0_HI 0x2e
#define PCI_CB_IO_LIMIT_0 0x30
#define PCI_CB_IO_LIMIT_0_HI 0x32
#define PCI_CB_IO_BASE_1 0x34
#define PCI_CB_IO_BASE_1_HI 0x36
#define PCI_CB_IO_LIMIT_1 0x38
#define PCI_CB_IO_LIMIT_1_HI 0x3a
#define PCI_CB_IO_RANGE_MASK ~0x03
/* 0x3c-0x3d are same as for htype 0 */
#define PCI_CB_BRIDGE_CONTROL 0x3e
#define PCI_CB_BRIDGE_CTL_PARITY 0x01 /* Similar to standard bridge control register */
#define PCI_CB_BRIDGE_CTL_SERR 0x02
#define PCI_CB_BRIDGE_CTL_ISA 0x04
#define PCI_CB_BRIDGE_CTL_VGA 0x08
#define PCI_CB_BRIDGE_CTL_MASTER_ABORT 0x20
#define PCI_CB_BRIDGE_CTL_CB_RESET 0x40 /* CardBus reset */
#define PCI_CB_BRIDGE_CTL_16BIT_INT 0x80 /* Enable interrupt for 16-bit cards */
#define PCI_CB_BRIDGE_CTL_PREFETCH_MEM0 0x100 /* Prefetch enable for both memory regions */
#define PCI_CB_BRIDGE_CTL_PREFETCH_MEM1 0x200
#define PCI_CB_BRIDGE_CTL_POST_WRITES 0x400
#define PCI_CB_SUBSYSTEM_VENDOR_ID 0x40
#define PCI_CB_SUBSYSTEM_ID 0x42
#define PCI_CB_LEGACY_MODE_BASE 0x44 /* 16-bit PC Card legacy mode base address (ExCa) */
/* 0x48-0x7f reserved */
/* Capability lists */
#define PCI_CAP_LIST_ID 0 /* Capability ID */
#define PCI_CAP_ID_PM 0x01 /* Power Management */
#define PCI_CAP_ID_AGP 0x02 /* Accelerated Graphics Port */
#define PCI_CAP_ID_VPD 0x03 /* Vital Product Data */
#define PCI_CAP_ID_SLOTID 0x04 /* Slot Identification */
#define PCI_CAP_ID_MSI 0x05 /* Message Signalled Interrupts */
#define PCI_CAP_ID_CHSWP 0x06 /* CompactPCI HotSwap */
#define PCI_CAP_ID_PCIX 0x07 /* PCI-X */
#define PCI_CAP_ID_HT 0x08 /* HyperTransport */
#define PCI_CAP_ID_VNDR 0x09 /* Vendor-Specific */
#define PCI_CAP_ID_DBG 0x0A /* Debug port */
#define PCI_CAP_ID_CCRC 0x0B /* CompactPCI Central Resource Control */
#define PCI_CAP_ID_SHPC 0x0C /* PCI Standard Hot-Plug Controller */
#define PCI_CAP_ID_SSVID 0x0D /* Bridge subsystem vendor/device ID */
#define PCI_CAP_ID_AGP3 0x0E /* AGP Target PCI-PCI bridge */
#define PCI_CAP_ID_SECDEV 0x0F /* Secure Device */
#define PCI_CAP_ID_EXP 0x10 /* PCI Express */
#define PCI_CAP_ID_MSIX 0x11 /* MSI-X */
#define PCI_CAP_ID_SATA 0x12 /* SATA Data/Index Conf. */
#define PCI_CAP_ID_AF 0x13 /* PCI Advanced Features */
#define PCI_CAP_ID_EA 0x14 /* PCI Enhanced Allocation */
#define PCI_CAP_ID_MAX PCI_CAP_ID_EA
#define PCI_CAP_LIST_NEXT 1 /* Next capability in the list */
#define PCI_CAP_FLAGS 2 /* Capability defined flags (16 bits) */
#define PCI_CAP_SIZEOF 4
/* Power Management Registers */
#define PCI_PM_CAP_VER_MASK 0x0007 /* Version */
#define PCI_PM_CAP_PME_CLOCK 0x0008 /* PME clock required */
#define PCI_PM_CAP_AUX_POWER 0x0010 /* Auxilliary power support */
#define PCI_PM_CAP_DSI 0x0020 /* Device specific initialization */
#define PCI_PM_CAP_D1 0x0200 /* D1 power state support */
#define PCI_PM_CAP_D2 0x0400 /* D2 power state support */
#define PCI_PM_CAP_PME 0x0800 /* PME pin supported */
#define PCI_PM_CTRL 4 /* PM control and status register */
#define PCI_PM_CTRL_STATE_MASK 0x0003 /* Current power state (D0 to D3) */
#define PCI_PM_CTRL_PME_ENABLE 0x0100 /* PME pin enable */
#define PCI_PM_CTRL_DATA_SEL_MASK 0x1e00 /* Data select (??) */
#define PCI_PM_CTRL_DATA_SCALE_MASK 0x6000 /* Data scale (??) */
#define PCI_PM_CTRL_PME_STATUS 0x8000 /* PME pin status */
#define PCI_PM_PPB_EXTENSIONS 6 /* PPB support extensions (??) */
#define PCI_PM_PPB_B2_B3 0x40 /* Stop clock when in D3hot (??) */
#define PCI_PM_BPCC_ENABLE 0x80 /* Bus power/clock control enable (??) */
#define PCI_PM_DATA_REGISTER 7 /* (??) */
#define PCI_PM_SIZEOF 8
/* AGP registers */
#define PCI_AGP_VERSION 2 /* BCD version number */
#define PCI_AGP_RFU 3 /* Rest of capability flags */
#define PCI_AGP_STATUS 4 /* Status register */
#define PCI_AGP_STATUS_RQ_MASK 0xff000000 /* Maximum number of requests - 1 */
#define PCI_AGP_STATUS_SBA 0x0200 /* Sideband addressing supported */
#define PCI_AGP_STATUS_64BIT 0x0020 /* 64-bit addressing supported */
#define PCI_AGP_STATUS_FW 0x0010 /* FW transfers supported */
#define PCI_AGP_STATUS_RATE4 0x0004 /* 4x transfer rate supported */
#define PCI_AGP_STATUS_RATE2 0x0002 /* 2x transfer rate supported */
#define PCI_AGP_STATUS_RATE1 0x0001 /* 1x transfer rate supported */
#define PCI_AGP_COMMAND 8 /* Control register */
#define PCI_AGP_COMMAND_RQ_MASK 0xff000000 /* Master: Maximum number of requests */
#define PCI_AGP_COMMAND_SBA 0x0200 /* Sideband addressing enabled */
#define PCI_AGP_COMMAND_AGP 0x0100 /* Allow processing of AGP transactions */
#define PCI_AGP_COMMAND_64BIT 0x0020 /* Allow processing of 64-bit addresses */
#define PCI_AGP_COMMAND_FW 0x0010 /* Force FW transfers */
#define PCI_AGP_COMMAND_RATE4 0x0004 /* Use 4x rate */
#define PCI_AGP_COMMAND_RATE2 0x0002 /* Use 4x rate */
#define PCI_AGP_COMMAND_RATE1 0x0001 /* Use 4x rate */
#define PCI_AGP_SIZEOF 12
/* PCI-X registers */
#define PCI_X_CMD_DPERR_E 0x0001 /* Data Parity Error Recovery Enable */
#define PCI_X_CMD_ERO 0x0002 /* Enable Relaxed Ordering */
#define PCI_X_CMD_MAX_READ 0x0000 /* Max Memory Read Byte Count */
#define PCI_X_CMD_MAX_SPLIT 0x0030 /* Max Outstanding Split Transactions */
#define PCI_X_CMD_VERSION(x) (((x) >> 12) & 3) /* Version */
/* Slot Identification */
#define PCI_SID_ESR 2 /* Expansion Slot Register */
#define PCI_SID_ESR_NSLOTS 0x1f /* Number of expansion slots available */
#define PCI_SID_ESR_FIC 0x20 /* First In Chassis Flag */
#define PCI_SID_CHASSIS_NR 3 /* Chassis Number */
/* Message Signalled Interrupts registers */
#define PCI_MSI_FLAGS 2 /* Various flags */
#define PCI_MSI_FLAGS_64BIT 0x80 /* 64-bit addresses allowed */
#define PCI_MSI_FLAGS_QSIZE 0x70 /* Message queue size configured */
#define PCI_MSI_FLAGS_QMASK 0x0e /* Maximum queue size available */
#define PCI_MSI_FLAGS_ENABLE 0x01 /* MSI feature enabled */
#define PCI_MSI_FLAGS_MASKBIT 0x0100 /* Per-vector masking capable */
#define PCI_MSI_RFU 3 /* Rest of capability flags */
#define PCI_MSI_ADDRESS_LO 4 /* Lower 32 bits */
#define PCI_MSI_ADDRESS_HI 8 /* Upper 32 bits (if PCI_MSI_FLAGS_64BIT set) */
#define PCI_MSI_DATA_32 8 /* 16 bits of data for 32-bit devices */
#define PCI_MSI_DATA_64 12 /* 16 bits of data for 64-bit devices */
#define PCI_MAX_PCI_DEVICES 32
#define PCI_MAX_PCI_FUNCTIONS 8
#define PCI_FIND_CAP_TTL 0x48
#define CAP_START_POS 0x40
/* Extended Capabilities (PCI-X 2.0 and Express) */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID(header) (header & 0x0000ffff)
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_VER(header) ((header >> 16) & 0xf)
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_NEXT(header) ((header >> 20) & 0xffc)
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_ERR 0x01 /* Advanced Error Reporting */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_VC 0x02 /* Virtual Channel Capability */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_DSN 0x03 /* Device Serial Number */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_PWR 0x04 /* Power Budgeting */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_RCLD 0x05 /* Root Complex Link Declaration */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_RCILC 0x06 /* Root Complex Internal Link Control */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_RCEC 0x07 /* Root Complex Event Collector */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_MFVC 0x08 /* Multi-Function VC Capability */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_VC9 0x09 /* same as _VC */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_RCRB 0x0A /* Root Complex RB? */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_VNDR 0x0B /* Vendor-Specific */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_CAC 0x0C /* Config Access - obsolete */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_ACS 0x0D /* Access Control Services */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_ARI 0x0E /* Alternate Routing ID */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_ATS 0x0F /* Address Translation Services */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_SRIOV 0x10 /* Single Root I/O Virtualization */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_MRIOV 0x11 /* Multi Root I/O Virtualization */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_MCAST 0x12 /* Multicast */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_PRI 0x13 /* Page Request Interface */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_AMD_XXX 0x14 /* Reserved for AMD */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_REBAR 0x15 /* Resizable BAR */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_DPA 0x16 /* Dynamic Power Allocation */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_TPH 0x17 /* TPH Requester */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_LTR 0x18 /* Latency Tolerance Reporting */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_SECPCI 0x19 /* Secondary PCIe Capability */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_PMUX 0x1A /* Protocol Multiplexing */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_PASID 0x1B /* Process Address Space ID */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_DPC 0x1D /* Downstream Port Containment */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_L1SS 0x1E /* L1 PM Substates */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_PTM 0x1F /* Precision Time Measurement */
#define PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_MAX PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_PTM
/* Enhanced Allocation Registers */
#define PCI_EA_NUM_ENT 2 /* Number of Capability Entries */
#define PCI_EA_NUM_ENT_MASK 0x3f /* Num Entries Mask */
#define PCI_EA_FIRST_ENT 4 /* First EA Entry in List */
#define PCI_EA_ES 0x00000007 /* Entry Size */
#define PCI_EA_BEI 0x000000f0 /* BAR Equivalent Indicator */
/* 9-14 map to VF BARs 0-5 respectively */
#define PCI_EA_BEI_VF_BAR0 9
#define PCI_EA_BEI_VF_BAR5 14
/* Base, MaxOffset registers */
/* bit 0 is reserved */
#define PCI_EA_IS_64 0x00000002 /* 64-bit field flag */
#define PCI_EA_FIELD_MASK 0xfffffffc /* For Base & Max Offset */
/* PCI Express capabilities */
#define PCI_EXP_FLAGS 2 /* Capabilities register */
#define PCI_EXP_FLAGS_VERS 0x000f /* Capability Version */
#define PCI_EXP_FLAGS_TYPE 0x00f0 /* Device/Port type */
#define PCI_EXP_TYPE_ROOT_PORT 0x4 /* Root Port */
#define PCI_EXP_TYPE_DOWNSTREAM 0x6 /* Downstream Port */
#define PCI_EXP_TYPE_PCIE_BRIDGE 0x8 /* PCI/PCI-X to PCIe Bridge */
#define PCI_EXP_DEVCAP 4 /* Device capabilities */
#define PCI_EXP_DEVCAP_FLR 0x10000000 /* Function Level Reset */
#define PCI_EXP_DEVCTL 8 /* Device Control */
#define PCI_EXP_DEVCTL_PAYLOAD 0x00e0 /* Max_Payload_Size */
#define PCI_EXP_DEVCTL_PAYLOAD_128B 0x0000 /* 128 Bytes */
#define PCI_EXP_DEVCTL_PAYLOAD_256B 0x0020 /* 256 Bytes */
#define PCI_EXP_DEVCTL_PAYLOAD_512B 0x0040 /* 512 Bytes */
#define PCI_EXP_DEVCTL_PAYLOAD_1024B 0x0060 /* 1024 Bytes */
#define PCI_EXP_DEVCTL_PAYLOAD_2048B 0x0080 /* 2048 Bytes */
#define PCI_EXP_DEVCTL_PAYLOAD_4096B 0x00a0 /* 4096 Bytes */
#define PCI_EXP_DEVCTL_RELAX_EN 0x0010 /* Enable relaxed ordering */
#define PCI_EXP_DEVCTL_NOSNOOP_EN 0x0800 /* Enable No Snoop */
#define PCI_EXP_DEVCTL_READRQ 0x7000 /* Max_Read_Request_Size */
#define PCI_EXP_DEVCTL_READRQ_128B 0x0000 /* 128 Bytes */
#define PCI_EXP_DEVCTL_READRQ_256B 0x1000 /* 256 Bytes */
#define PCI_EXP_DEVCTL_READRQ_512B 0x2000 /* 512 Bytes */
#define PCI_EXP_DEVCTL_READRQ_1024B 0x3000 /* 1024 Bytes */
#define PCI_EXP_DEVCTL_READRQ_2048B 0x4000 /* 2048 Bytes */
#define PCI_EXP_DEVCTL_READRQ_4096B 0x5000 /* 4096 Bytes */
#define PCI_EXP_DEVCTL_BCR_FLR 0x8000 /* Bridge Configuration Retry / FLR */
#define PCI_EXP_LNKCAP 12 /* Link Capabilities */
#define PCI_EXP_LNKCAP_SLS 0x0000000f /* Supported Link Speeds */
#define PCI_EXP_LNKCAP_SLS_2_5GB 0x00000001 /* LNKCAP2 SLS Vector bit 0 */
#define PCI_EXP_LNKCAP_SLS_5_0GB 0x00000002 /* LNKCAP2 SLS Vector bit 1 */
#define PCI_EXP_LNKCAP_SLS_8_0GB 0x00000003 /* LNKCAP2 SLS Vector bit 2 */
#define PCI_EXP_LNKCAP_MLW 0x000003f0 /* Maximum Link Width */
#define PCI_EXP_LNKCAP_DLLLARC 0x00100000 /* Data Link Layer Link Active Reporting Capable */
#define PCI_EXP_LNKCTL 16 /* Link Control */
#define PCI_EXP_LNKCTL_RL 0x0020 /* Retrain Link */
#define PCI_EXP_LNKSTA 18 /* Link Status */
#define PCI_EXP_LNKSTA_CLS 0x000f /* Current Link Speed */
#define PCI_EXP_LNKSTA_CLS_2_5GB 0x0001 /* Current Link Speed 2.5GT/s */
#define PCI_EXP_LNKSTA_CLS_5_0GB 0x0002 /* Current Link Speed 5.0GT/s */
#define PCI_EXP_LNKSTA_CLS_8_0GB 0x0003 /* Current Link Speed 8.0GT/s */
#define PCI_EXP_LNKSTA_NLW 0x03f0 /* Negotiated Link Width */
#define PCI_EXP_LNKSTA_NLW_SHIFT 4 /* start of NLW mask in link status */
#define PCI_EXP_LNKSTA_LT 0x0800 /* Link Training */
#define PCI_EXP_LNKSTA_DLLLA 0x2000 /* Data Link Layer Link Active */
#define PCI_EXP_LNKSTA_LBMS 0x4000 /* Link Bandwidth Management Status */
#define PCI_EXP_SLTCAP 20 /* Slot Capabilities */
#define PCI_EXP_SLTCAP_PSN 0xfff80000 /* Physical Slot Number */
#define PCI_EXP_RTCTL 28 /* Root Control */
#define PCI_EXP_RTCTL_CRSSVE 0x0010 /* CRS Software Visibility Enable */
#define PCI_EXP_RTCAP 30 /* Root Capabilities */
#define PCI_EXP_RTCAP_CRSVIS 0x0001 /* CRS Software Visibility capability */
#define PCI_EXP_DEVCAP2 36 /* Device Capabilities 2 */
#define PCI_EXP_DEVCAP2_ARI 0x00000020 /* ARI Forwarding Supported */
#define PCI_EXP_DEVCTL2 40 /* Device Control 2 */
#define PCI_EXP_DEVCTL2_ARI 0x0020 /* Alternative Routing-ID */
#define PCI_EXP_LNKCAP2 44 /* Link Capability 2 */
#define PCI_EXP_LNKCAP2_SLS 0x000000fe /* Supported Link Speeds Vector */
#define PCI_EXP_LNKCTL2 48 /* Link Control 2 */
#define PCI_EXP_LNKCTL2_TLS 0x000f /* Target Link Speed */
#define PCI_EXP_LNKCTL2_TLS_2_5GT 0x0001 /* Target Link Speed 2.5GT/s */
#define PCI_EXP_LNKCTL2_TLS_5_0GT 0x0002 /* Target Link Speed 5.0GT/s */
#define PCI_EXP_LNKCTL2_TLS_8_0GT 0x0003 /* Target Link Speed 8.0GT/s */
/* Advanced Error Reporting */
#define PCI_ERR_CAP 24 /* Advanced Error Capabilities */
#define PCI_ERR_CAP_FEP(x) ((x) & 31) /* First Error Pointer */
#define PCI_ERR_CAP_ECRC_GENC 0x00000020 /* ECRC Generation Capable */
#define PCI_ERR_CAP_ECRC_GENE 0x00000040 /* ECRC Generation Enable */
#define PCI_ERR_CAP_ECRC_CHKC 0x00000080 /* ECRC Check Capable */
#define PCI_ERR_CAP_ECRC_CHKE 0x00000100 /* ECRC Check Enable */
/* Single Root I/O Virtualization Registers */
#define PCI_SRIOV_CAP 0x04 /* SR-IOV Capabilities */
#define PCI_SRIOV_CTRL 0x08 /* SR-IOV Control */
#define PCI_SRIOV_CTRL_VFE 0x01 /* VF Enable */
#define PCI_SRIOV_CTRL_MSE 0x08 /* VF Memory Space Enable */
#define PCI_SRIOV_CTRL_ARI 0x10 /* ARI Capable Hierarchy */
#define PCI_SRIOV_INITIAL_VF 0x0c /* Initial VFs */
#define PCI_SRIOV_TOTAL_VF 0x0e /* Total VFs */
#define PCI_SRIOV_NUM_VF 0x10 /* Number of VFs */
#define PCI_SRIOV_VF_OFFSET 0x14 /* First VF Offset */
#define PCI_SRIOV_VF_STRIDE 0x16 /* Following VF Stride */
#define PCI_SRIOV_VF_DID 0x1a /* VF Device ID */
/* Include the ID list */
#include <pci_ids.h>
/*
* Config Address for PCI Configuration Mechanism #1
*
* See PCI Local Bus Specification, Revision 3.0,
* Section 3.2.2.3.2, Figure 3-2, p. 50.
*/
#define PCI_CONF1_BUS_SHIFT 16 /* Bus number */
#define PCI_CONF1_DEV_SHIFT 11 /* Device number */
#define PCI_CONF1_FUNC_SHIFT 8 /* Function number */
#define PCI_CONF1_BUS_MASK 0xff
#define PCI_CONF1_DEV_MASK 0x1f
#define PCI_CONF1_FUNC_MASK 0x7
#define PCI_CONF1_REG_MASK 0xfc /* Limit aligned offset to a maximum of 256B */
#define PCI_CONF1_ENABLE BIT(31)
#define PCI_CONF1_BUS(x) (((x) & PCI_CONF1_BUS_MASK) << PCI_CONF1_BUS_SHIFT)
#define PCI_CONF1_DEV(x) (((x) & PCI_CONF1_DEV_MASK) << PCI_CONF1_DEV_SHIFT)
#define PCI_CONF1_FUNC(x) (((x) & PCI_CONF1_FUNC_MASK) << PCI_CONF1_FUNC_SHIFT)
#define PCI_CONF1_REG(x) ((x) & PCI_CONF1_REG_MASK)
#define PCI_CONF1_ADDRESS(bus, dev, func, reg) \
(PCI_CONF1_ENABLE | \
PCI_CONF1_BUS(bus) | \
PCI_CONF1_DEV(dev) | \
PCI_CONF1_FUNC(func) | \
PCI_CONF1_REG(reg))
/*
* Extension of PCI Config Address for accessing extended PCIe registers
*
* No standardized specification, but used on lot of non-ECAM-compliant ARM SoCs
* or on AMD Barcelona and new CPUs. Reserved bits [27:24] of PCI Config Address
* are used for specifying additional 4 high bits of PCI Express register.
*/
#define PCI_CONF1_EXT_REG_SHIFT 16
#define PCI_CONF1_EXT_REG_MASK 0xf00
#define PCI_CONF1_EXT_REG(x) (((x) & PCI_CONF1_EXT_REG_MASK) << PCI_CONF1_EXT_REG_SHIFT)
#define PCI_CONF1_EXT_ADDRESS(bus, dev, func, reg) \
(PCI_CONF1_ADDRESS(bus, dev, func, reg) | \
PCI_CONF1_EXT_REG(reg))
/*
* Enhanced Configuration Access Mechanism (ECAM)
*
* See PCI Express Base Specification, Revision 5.0, Version 1.0,
* Section 7.2.2, Table 7-1, p. 677.
*/
#define PCIE_ECAM_BUS_SHIFT 20 /* Bus number */
#define PCIE_ECAM_DEV_SHIFT 15 /* Device number */
#define PCIE_ECAM_FUNC_SHIFT 12 /* Function number */
#define PCIE_ECAM_BUS_MASK 0xff
#define PCIE_ECAM_DEV_MASK 0x1f
#define PCIE_ECAM_FUNC_MASK 0x7
#define PCIE_ECAM_REG_MASK 0xfff /* Limit offset to a maximum of 4K */
#define PCIE_ECAM_BUS(x) (((x) & PCIE_ECAM_BUS_MASK) << PCIE_ECAM_BUS_SHIFT)
#define PCIE_ECAM_DEV(x) (((x) & PCIE_ECAM_DEV_MASK) << PCIE_ECAM_DEV_SHIFT)
#define PCIE_ECAM_FUNC(x) (((x) & PCIE_ECAM_FUNC_MASK) << PCIE_ECAM_FUNC_SHIFT)
#define PCIE_ECAM_REG(x) ((x) & PCIE_ECAM_REG_MASK)
#define PCIE_ECAM_OFFSET(bus, dev, func, where) \
(PCIE_ECAM_BUS(bus) | \
PCIE_ECAM_DEV(dev) | \
PCIE_ECAM_FUNC(func) | \
PCIE_ECAM_REG(where))
#ifndef __ASSEMBLY__
#include <dm/pci.h>
#ifdef CONFIG_SYS_PCI_64BIT
typedef u64 pci_addr_t;
typedef u64 pci_size_t;
#else
typedef unsigned long pci_addr_t;
typedef unsigned long pci_size_t;
#endif
struct pci_region {
pci_addr_t bus_start; /* Start on the bus */
phys_addr_t phys_start; /* Start in physical address space */
pci_size_t size; /* Size */
unsigned long flags; /* Resource flags */
pci_addr_t bus_lower;
};
#define PCI_REGION_MEM 0x00000000 /* PCI memory space */
#define PCI_REGION_IO 0x00000001 /* PCI IO space */
#define PCI_REGION_TYPE 0x00000001
#define PCI_REGION_PREFETCH 0x00000008 /* prefetchable PCI memory */
#define PCI_REGION_SYS_MEMORY 0x00000100 /* System memory */
#define PCI_REGION_RO 0x00000200 /* Read-only memory */
static inline void pci_set_region(struct pci_region *reg,
pci_addr_t bus_start,
phys_addr_t phys_start,
pci_size_t size,
unsigned long flags) {
reg->bus_start = bus_start;
reg->phys_start = phys_start;
reg->size = size;
reg->flags = flags;
}
typedef int pci_dev_t;
#define PCI_BUS(d) (((d) >> 16) & 0xff)
/*
* Please note the difference in DEVFN usage in U-Boot vs Linux. U-Boot
* uses DEVFN in bits 15-8 but Linux instead expects DEVFN in bits 7-0.
* Please see the Linux header include/uapi/linux/pci.h for more details.
* This is relevant for the following macros:
* PCI_DEV, PCI_FUNC, PCI_DEVFN
* The U-Boot macro PCI_DEV is equivalent to the Linux PCI_SLOT version with
* the remark from above (input is in bits 15-8 instead of 7-0.
*/
#define PCI_DEV(d) (((d) >> 11) & 0x1f)
#define PCI_FUNC(d) (((d) >> 8) & 0x7)
#define PCI_DEVFN(d, f) ((d) << 11 | (f) << 8)
#define PCI_MASK_BUS(bdf) ((bdf) & 0xffff)
#define PCI_ADD_BUS(bus, devfn) (((bus) << 16) | (devfn))
#define PCI_BDF(b, d, f) ((b) << 16 | PCI_DEVFN(d, f))
#define PCI_ANY_ID (~0)
/* Convert from Linux format to U-Boot format */
#define PCI_TO_BDF(val) ((val) << 8)
struct pci_device_id {
unsigned int vendor, device; /* Vendor and device ID or PCI_ANY_ID */
unsigned int subvendor, subdevice; /* Subsystem ID's or PCI_ANY_ID */
unsigned int class, class_mask; /* (class,subclass,prog-if) triplet */
unsigned long driver_data; /* Data private to the driver */
};
struct pci_controller;
struct pci_config_table {
unsigned int vendor, device; /* Vendor and device ID or PCI_ANY_ID */
unsigned int class; /* Class ID, or PCI_ANY_ID */
unsigned int bus; /* Bus number, or PCI_ANY_ID */
unsigned int dev; /* Device number, or PCI_ANY_ID */
unsigned int func; /* Function number, or PCI_ANY_ID */
void (*config_device)(struct pci_controller* hose, pci_dev_t dev,
struct pci_config_table *);
unsigned long priv[3];
};
extern void pci_cfgfunc_do_nothing(struct pci_controller* hose, pci_dev_t dev,
struct pci_config_table *);
extern void pci_cfgfunc_config_device(struct pci_controller* hose, pci_dev_t dev,
struct pci_config_table *);
#define INDIRECT_TYPE_NO_PCIE_LINK 1
/**
* Structure of a PCI controller (host bridge)
*
* With driver model this is dev_get_uclass_priv(bus)
*
* @skip_auto_config_until_reloc: true to avoid auto-config until U-Boot has
* relocated. Normally if PCI is used before relocation, this happens
* before relocation also. Some platforms set up static configuration in
* TPL/SPL to reduce code size and boot time, since these phases only know
* about a small subset of PCI devices. This is normally false.
*/
struct pci_controller {
struct udevice *bus;
struct udevice *ctlr;
bool skip_auto_config_until_reloc;
int first_busno;
int last_busno;
volatile unsigned int *cfg_addr;
volatile unsigned char *cfg_data;
int indirect_type;
/*
* TODO(sjg@chromium.org): With driver model we use struct
* pci_controller for both the controller and any bridge devices
* attached to it. But there is only one region list and it is in the
* top-level controller.
*
* This could be changed so that struct pci_controller is only used
* for PCI controllers and a separate UCLASS (or perhaps
* UCLASS_PCI_GENERIC) is used for bridges.
*/
struct pci_region *regions;
int region_count;
struct pci_config_table *config_table;
void (*fixup_irq)(struct pci_controller *, pci_dev_t);
/* Used by auto config */
struct pci_region *pci_mem, *pci_io, *pci_prefetch;
};
#if defined(CONFIG_DM_PCI_COMPAT)
extern phys_addr_t pci_hose_bus_to_phys(struct pci_controller* hose,
pci_addr_t addr, unsigned long flags);
extern pci_addr_t pci_hose_phys_to_bus(struct pci_controller* hose,
phys_addr_t addr, unsigned long flags);
#define pci_phys_to_bus(dev, addr, flags) \
pci_hose_phys_to_bus(pci_bus_to_hose(PCI_BUS(dev)), (addr), (flags))
#define pci_bus_to_phys(dev, addr, flags) \
pci_hose_bus_to_phys(pci_bus_to_hose(PCI_BUS(dev)), (addr), (flags))
#define pci_virt_to_bus(dev, addr, flags) \
pci_hose_phys_to_bus(pci_bus_to_hose(PCI_BUS(dev)), \
(virt_to_phys(addr)), (flags))
#define pci_bus_to_virt(dev, addr, flags, len, map_flags) \
map_physmem(pci_hose_bus_to_phys(pci_bus_to_hose(PCI_BUS(dev)), \
(addr), (flags)), \
(len), (map_flags))
#define pci_phys_to_mem(dev, addr) \
pci_phys_to_bus((dev), (addr), PCI_REGION_MEM)
#define pci_mem_to_phys(dev, addr) \
pci_bus_to_phys((dev), (addr), PCI_REGION_MEM)
#define pci_phys_to_io(dev, addr) pci_phys_to_bus((dev), (addr), PCI_REGION_IO)
#define pci_io_to_phys(dev, addr) pci_bus_to_phys((dev), (addr), PCI_REGION_IO)
#define pci_virt_to_mem(dev, addr) \
pci_virt_to_bus((dev), (addr), PCI_REGION_MEM)
#define pci_mem_to_virt(dev, addr, len, map_flags) \
pci_bus_to_virt((dev), (addr), PCI_REGION_MEM, (len), (map_flags))
#define pci_virt_to_io(dev, addr) \
pci_virt_to_bus((dev), (addr), PCI_REGION_IO)
#define pci_io_to_virt(dev, addr, len, map_flags) \
pci_bus_to_virt((dev), (addr), PCI_REGION_IO, (len), (map_flags))
/* For driver model these are defined in macros in pci_compat.c */
extern int pci_hose_read_config_byte(struct pci_controller *hose,
pci_dev_t dev, int where, u8 *val);
extern int pci_hose_read_config_word(struct pci_controller *hose,
pci_dev_t dev, int where, u16 *val);
extern int pci_hose_read_config_dword(struct pci_controller *hose,
pci_dev_t dev, int where, u32 *val);
extern int pci_hose_write_config_byte(struct pci_controller *hose,
pci_dev_t dev, int where, u8 val);
extern int pci_hose_write_config_word(struct pci_controller *hose,
pci_dev_t dev, int where, u16 val);
extern int pci_hose_write_config_dword(struct pci_controller *hose,
pci_dev_t dev, int where, u32 val);
#endif
void pciauto_region_init(struct pci_region *res);
void pciauto_region_align(struct pci_region *res, pci_size_t size);
void pciauto_config_init(struct pci_controller *hose);
/**
* pciauto_region_allocate() - Allocate resources from a PCI resource region
*
* Allocates @size bytes from the PCI resource @res. If @supports_64bit is
* false, the result will be guaranteed to fit in 32 bits.
*
* @res: PCI region to allocate from
* @size: Amount of bytes to allocate
* @bar: Returns the PCI bus address of the allocated resource
* @supports_64bit: Whether to allow allocations above the 32-bit boundary
* Return: 0 if successful, -1 on failure
*/
int pciauto_region_allocate(struct pci_region *res, pci_size_t size,
pci_addr_t *bar, bool supports_64bit);
int pci_skip_dev(struct pci_controller *hose, pci_dev_t dev);
#if defined(CONFIG_DM_PCI_COMPAT)
extern int pci_hose_read_config_byte_via_dword(struct pci_controller *hose,
pci_dev_t dev, int where, u8 *val);
extern int pci_hose_read_config_word_via_dword(struct pci_controller *hose,
pci_dev_t dev, int where, u16 *val);
extern int pci_hose_write_config_byte_via_dword(struct pci_controller *hose,
pci_dev_t dev, int where, u8 val);
extern int pci_hose_write_config_word_via_dword(struct pci_controller *hose,
pci_dev_t dev, int where, u16 val);
extern void *pci_map_bar(pci_dev_t pdev, int bar, int flags);
extern void pci_register_hose(struct pci_controller* hose);
extern struct pci_controller* pci_bus_to_hose(int bus);
extern struct pci_controller *find_hose_by_cfg_addr(void *cfg_addr);
extern struct pci_controller *pci_get_hose_head(void);
extern int pci_hose_scan(struct pci_controller *hose);
extern int pci_hose_scan_bus(struct pci_controller *hose, int bus);
extern void pciauto_setup_device(struct pci_controller *hose,
pci_dev_t dev, int bars_num,
struct pci_region *mem,
struct pci_region *prefetch,
struct pci_region *io);
extern void pciauto_prescan_setup_bridge(struct pci_controller *hose,
pci_dev_t dev, int sub_bus);
extern void pciauto_postscan_setup_bridge(struct pci_controller *hose,
pci_dev_t dev, int sub_bus);
extern int pciauto_config_device(struct pci_controller *hose, pci_dev_t dev);
extern pci_dev_t pci_find_device (unsigned int vendor, unsigned int device, int index);
extern pci_dev_t pci_find_devices (struct pci_device_id *ids, int index);
pci_dev_t pci_find_class(unsigned int find_class, int index);
extern int pci_hose_find_capability(struct pci_controller *hose, pci_dev_t dev,
int cap);
extern int pci_hose_find_cap_start(struct pci_controller *hose, pci_dev_t dev,
u8 hdr_type);
extern int pci_find_cap(struct pci_controller *hose, pci_dev_t dev, int pos,
int cap);
int pci_find_next_ext_capability(struct pci_controller *hose,
pci_dev_t dev, int start, int cap);
int pci_hose_find_ext_capability(struct pci_controller *hose,
pci_dev_t dev, int cap);
#endif /* defined(CONFIG_DM_PCI_COMPAT) */
const char * pci_class_str(u8 class);
int pci_last_busno(void);
#ifdef CONFIG_MPC85xx
extern void pci_mpc85xx_init (struct pci_controller *hose);
#endif
/**
* pci_write_bar32() - Write the address of a BAR including control bits
*
* This writes a raw address (with control bits) to a bar. This can be used
* with devices which require hard-coded addresses, not part of the normal
* PCI enumeration process.
*
* This is only available if CONFIG_DM_PCI_COMPAT is enabled
*
* @hose: PCI hose to use
* @dev: PCI device to update
* @barnum: BAR number (0-5)
* @addr: BAR address with control bits
*/
void pci_write_bar32(struct pci_controller *hose, pci_dev_t dev, int barnum,
u32 addr);
/**
* pci_read_bar32() - read the address of a bar
*
* This is only available if CONFIG_DM_PCI_COMPAT is enabled
*
* @hose: PCI hose to use
* @dev: PCI device to inspect
* @barnum: BAR number (0-5)
* Return: address of the bar, masking out any control bits
* */
u32 pci_read_bar32(struct pci_controller *hose, pci_dev_t dev, int barnum);
/**
* pci_hose_find_devices() - Find devices by vendor/device ID
*
* This is only available if CONFIG_DM_PCI_COMPAT is enabled
*
* @hose: PCI hose to search
* @busnum: Bus number to search
* @ids: PCI vendor/device IDs to look for, terminated by 0, 0 record
* @indexp: Pointer to device index to find. To find the first matching
* device, pass 0; to find the second, pass 1, etc. This
* parameter is decremented for each non-matching device so
* can be called repeatedly.
*/
pci_dev_t pci_hose_find_devices(struct pci_controller *hose, int busnum,
struct pci_device_id *ids, int *indexp);
/* Access sizes for PCI reads and writes */
enum pci_size_t {
PCI_SIZE_8,
PCI_SIZE_16,
PCI_SIZE_32,
};
struct udevice;
/**
* struct pci_child_plat - information stored about each PCI device
*
* Every device on a PCI bus has this per-child data.
*
* It can be accessed using dev_get_parent_plat(dev) if dev->parent is a
* PCI bus (i.e. UCLASS_PCI)
*
* @devfn: Encoded device and function index - see PCI_DEVFN()
* @vendor: PCI vendor ID (see pci_ids.h)
* @device: PCI device ID (see pci_ids.h)
* @class: PCI class, 3 bytes: (base, sub, prog-if)
* @is_virtfn: True for Virtual Function device
* @pfdev: Handle to Physical Function device
* @virtid: Virtual Function Index
*/
struct pci_child_plat {
int devfn;
unsigned short vendor;
unsigned short device;
unsigned int class;
/* Variables for CONFIG_PCI_SRIOV */
bool is_virtfn;
struct udevice *pfdev;
int virtid;
};
/* PCI bus operations */
struct dm_pci_ops {
/**
* read_config() - Read a PCI configuration value
*
* PCI buses must support reading and writing configuration values
* so that the bus can be scanned and its devices configured.
*
* Normally PCI_BUS(@bdf) is the same as @dev_seq(bus), but not always.
* If bridges exist it is possible to use the top-level bus to
* access a sub-bus. In that case @bus will be the top-level bus
* and PCI_BUS(bdf) will be a different (higher) value
*
* @bus: Bus to read from
* @bdf: Bus, device and function to read
* @offset: Byte offset within the device's configuration space
* @valuep: Place to put the returned value
* @size: Access size
* @return 0 if OK, -ve on error
*/
int (*read_config)(const struct udevice *bus, pci_dev_t bdf,
uint offset, ulong *valuep, enum pci_size_t size);
/**
* write_config() - Write a PCI configuration value
*
* @bus: Bus to write to
* @bdf: Bus, device and function to write
* @offset: Byte offset within the device's configuration space
* @value: Value to write
* @size: Access size
* @return 0 if OK, -ve on error
*/
int (*write_config)(const struct udevice *bus, pci_dev_t bdf, uint offset,
ulong value, enum pci_size_t size);
};
/* Get access to a PCI bus' operations */
#define pci_get_ops(dev) ((struct dm_pci_ops *)(dev)->driver->ops)
/**
* dm_pci_get_bdf() - Get the BDF value for a device
*
* @dev: Device to check
* Return: bus/device/function value (see PCI_BDF())
*/
pci_dev_t dm_pci_get_bdf(const struct udevice *dev);
/**
* pci_bind_bus_devices() - scan a PCI bus and bind devices
*
* Scan a PCI bus looking for devices. Bind each one that is found. If
* devices are already bound that match the scanned devices, just update the
* child data so that the device can be used correctly (this happens when
* the device tree describes devices we expect to see on the bus).
*
* Devices that are bound in this way will use a generic PCI driver which
* does nothing. The device can still be accessed but will not provide any
* driver interface.
*
* @bus: Bus containing devices to bind
* Return: 0 if OK, -ve on error
*/
int pci_bind_bus_devices(struct udevice *bus);
/**
* pci_auto_config_devices() - configure bus devices ready for use
*
* This works through all devices on a bus by scanning the driver model
* data structures (normally these have been set up by pci_bind_bus_devices()
* earlier).
*
* Space is allocated for each PCI base address register (BAR) so that the
* devices are mapped into memory and I/O space ready for use.
*
* @bus: Bus containing devices to bind
* Return: 0 if OK, -ve on error
*/
int pci_auto_config_devices(struct udevice *bus);
/**
* dm_pci_bus_find_bdf() - Find a device given its PCI bus address
*
* @bdf: PCI device address: bus, device and function -see PCI_BDF()
* @devp: Returns the device for this address, if found
* Return: 0 if OK, -ENODEV if not found
*/
int dm_pci_bus_find_bdf(pci_dev_t bdf, struct udevice **devp);
/**
* pci_bus_find_devfn() - Find a device on a bus
*
* @find_devfn: PCI device address (device and function only)
* @devp: Returns the device for this address, if found
* Return: 0 if OK, -ENODEV if not found
*/
int pci_bus_find_devfn(const struct udevice *bus, pci_dev_t find_devfn,
struct udevice **devp);
/**
* pci_find_first_device() - return the first available PCI device
*
* This function and pci_find_first_device() allow iteration through all
* available PCI devices on all buses. Assuming there are any, this will
* return the first one.
*
* @devp: Set to the first available device, or NULL if no more are left
* or we got an error
* Return: 0 if all is OK, -ve on error (e.g. a bus/bridge failed to probe)
*/
int pci_find_first_device(struct udevice **devp);
/**
* pci_find_next_device() - return the next available PCI device
*
* Finds the next available PCI device after the one supplied, or sets @devp
* to NULL if there are no more.
*
* @devp: On entry, the last device returned. Set to the next available
* device, or NULL if no more are left or we got an error
* Return: 0 if all is OK, -ve on error (e.g. a bus/bridge failed to probe)
*/
int pci_find_next_device(struct udevice **devp);
/**
* pci_get_ff() - Returns a mask for the given access size
*
* @size: Access size
* Return: 0xff for PCI_SIZE_8, 0xffff for PCI_SIZE_16, 0xffffffff for
* PCI_SIZE_32
*/
int pci_get_ff(enum pci_size_t size);
/**
* pci_bus_find_devices () - Find devices on a bus
*
* @bus: Bus to search
* @ids: PCI vendor/device IDs to look for, terminated by 0, 0 record
* @indexp: Pointer to device index to find. To find the first matching
* device, pass 0; to find the second, pass 1, etc. This
* parameter is decremented for each non-matching device so
* can be called repeatedly.
* @devp: Returns matching device if found
* Return: 0 if found, -ENODEV if not
*/
int pci_bus_find_devices(struct udevice *bus, const struct pci_device_id *ids,
int *indexp, struct udevice **devp);
/**
* pci_find_device_id() - Find a device on any bus
*
* @ids: PCI vendor/device IDs to look for, terminated by 0, 0 record
* @index: Index number of device to find, 0 for the first match, 1 for
* the second, etc.
* @devp: Returns matching device if found
* Return: 0 if found, -ENODEV if not
*/
int pci_find_device_id(const struct pci_device_id *ids, int index,
struct udevice **devp);
/**
* dm_pci_hose_probe_bus() - probe a subordinate bus, scanning it for devices
*
* This probes the given bus which causes it to be scanned for devices. The
* devices will be bound but not probed.
*
* @hose specifies the PCI hose that will be used for the scan. This is
* always a top-level bus with uclass UCLASS_PCI. The bus to scan is
* in @bdf, and is a subordinate bus reachable from @hose.
*
* @hose: PCI hose to scan
* @bdf: PCI bus address to scan (PCI_BUS(bdf) is the bus number)
* Return: 0 if OK, -ve on error
*/
int dm_pci_hose_probe_bus(struct udevice *bus);
/**
* pci_bus_read_config() - Read a configuration value from a device
*
* TODO(sjg@chromium.org): We should be able to pass just a device and have
* it do the right thing. It would be good to have that function also.
*
* @bus: Bus to read from
* @bdf: PCI device address: bus, device and function -see PCI_BDF()
* @offset: Register offset to read
* @valuep: Place to put the returned value
* @size: Access size
* Return: 0 if OK, -ve on error
*/
int pci_bus_read_config(const struct udevice *bus, pci_dev_t bdf, int offset,
unsigned long *valuep, enum pci_size_t size);
/**
* pci_bus_write_config() - Write a configuration value to a device
*
* @bus: Bus to write from
* @bdf: PCI device address: bus, device and function -see PCI_BDF()
* @offset: Register offset to write
* @value: Value to write
* @size: Access size
* Return: 0 if OK, -ve on error
*/
int pci_bus_write_config(struct udevice *bus, pci_dev_t bdf, int offset,
unsigned long value, enum pci_size_t size);
/**
* pci_bus_clrset_config32() - Update a configuration value for a device
*
* The register at @offset is updated to (oldvalue & ~clr) | set.
*
* @bus: Bus to access
* @bdf: PCI device address: bus, device and function -see PCI_BDF()
* @offset: Register offset to update
* @clr: Bits to clear
* @set: Bits to set
* Return: 0 if OK, -ve on error
*/
int pci_bus_clrset_config32(struct udevice *bus, pci_dev_t bdf, int offset,
u32 clr, u32 set);
/**
* Driver model PCI config access functions. Use these in preference to others
* when you have a valid device
*/
int dm_pci_read_config(const struct udevice *dev, int offset,
unsigned long *valuep, enum pci_size_t size);
int dm_pci_read_config8(const struct udevice *dev, int offset, u8 *valuep);
int dm_pci_read_config16(const struct udevice *dev, int offset, u16 *valuep);
int dm_pci_read_config32(const struct udevice *dev, int offset, u32 *valuep);
int dm_pci_write_config(struct udevice *dev, int offset, unsigned long value,
enum pci_size_t size);
int dm_pci_write_config8(struct udevice *dev, int offset, u8 value);
int dm_pci_write_config16(struct udevice *dev, int offset, u16 value);
int dm_pci_write_config32(struct udevice *dev, int offset, u32 value);
/**
* These permit convenient read/modify/write on PCI configuration. The
* register is updated to (oldvalue & ~clr) | set.
*/
int dm_pci_clrset_config8(struct udevice *dev, int offset, u32 clr, u32 set);
int dm_pci_clrset_config16(struct udevice *dev, int offset, u32 clr, u32 set);
int dm_pci_clrset_config32(struct udevice *dev, int offset, u32 clr, u32 set);
/*
* The following functions provide access to the above without needing the
* size parameter. We are trying to encourage the use of the 8/16/32-style
* functions, rather than byte/word/dword. But both are supported.
*/
int pci_write_config32(pci_dev_t pcidev, int offset, u32 value);
int pci_write_config16(pci_dev_t pcidev, int offset, u16 value);
int pci_write_config8(pci_dev_t pcidev, int offset, u8 value);
int pci_read_config32(pci_dev_t pcidev, int offset, u32 *valuep);
int pci_read_config16(pci_dev_t pcidev, int offset, u16 *valuep);
int pci_read_config8(pci_dev_t pcidev, int offset, u8 *valuep);
/**
* pci_generic_mmap_write_config() - Generic helper for writing to
* memory-mapped PCI configuration space.
* @bus: Pointer to the PCI bus
* @addr_f: Callback for calculating the config space address
* @bdf: Identifies the PCI device to access
* @offset: The offset into the device's configuration space
* @value: The value to write
* @size: Indicates the size of access to perform
*
* Write the value @value of size @size from offset @offset within the
* configuration space of the device identified by the bus, device & function
* numbers in @bdf on the PCI bus @bus. The callback function @addr_f is
* responsible for calculating the CPU address of the respective configuration
* space offset.
*
* Return: 0 on success, else -EINVAL
*/
int pci_generic_mmap_write_config(
const struct udevice *bus,
int (*addr_f)(const struct udevice *bus, pci_dev_t bdf, uint offset,
void **addrp),
pci_dev_t bdf,
uint offset,
ulong value,
enum pci_size_t size);
/**
* pci_generic_mmap_read_config() - Generic helper for reading from
* memory-mapped PCI configuration space.
* @bus: Pointer to the PCI bus
* @addr_f: Callback for calculating the config space address
* @bdf: Identifies the PCI device to access
* @offset: The offset into the device's configuration space
* @valuep: A pointer at which to store the read value
* @size: Indicates the size of access to perform
*
* Read a value of size @size from offset @offset within the configuration
* space of the device identified by the bus, device & function numbers in @bdf
* on the PCI bus @bus. The callback function @addr_f is responsible for
* calculating the CPU address of the respective configuration space offset.
*
* Return: 0 on success, else -EINVAL
*/
int pci_generic_mmap_read_config(
const struct udevice *bus,
int (*addr_f)(const struct udevice *bus, pci_dev_t bdf, uint offset,
void **addrp),
pci_dev_t bdf,
uint offset,
ulong *valuep,
enum pci_size_t size);
#if defined(CONFIG_PCI_SRIOV)
/**
* pci_sriov_init() - Scan Virtual Function devices
*
* @pdev: Physical Function udevice handle
* @vf_en: Number of Virtual Function devices to enable
* Return: 0 on success, -ve on error
*/
int pci_sriov_init(struct udevice *pdev, int vf_en);
/**
* pci_sriov_get_totalvfs() - Get total available Virtual Function devices
*
* @pdev: Physical Function udevice handle
* Return: count on success, -ve on error
*/
int pci_sriov_get_totalvfs(struct udevice *pdev);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_DM_PCI_COMPAT
/* Compatibility with old naming */
static inline int pci_write_config_dword(pci_dev_t pcidev, int offset,
u32 value)
{
return pci_write_config32(pcidev, offset, value);
}
/* Compatibility with old naming */
static inline int pci_write_config_word(pci_dev_t pcidev, int offset,
u16 value)
{
return pci_write_config16(pcidev, offset, value);
}
/* Compatibility with old naming */
static inline int pci_write_config_byte(pci_dev_t pcidev, int offset,
u8 value)
{
return pci_write_config8(pcidev, offset, value);
}
/* Compatibility with old naming */
static inline int pci_read_config_dword(pci_dev_t pcidev, int offset,
u32 *valuep)
{
return pci_read_config32(pcidev, offset, valuep);
}
/* Compatibility with old naming */
static inline int pci_read_config_word(pci_dev_t pcidev, int offset,
u16 *valuep)
{
return pci_read_config16(pcidev, offset, valuep);
}
/* Compatibility with old naming */
static inline int pci_read_config_byte(pci_dev_t pcidev, int offset,
u8 *valuep)
{
return pci_read_config8(pcidev, offset, valuep);
}
#endif /* CONFIG_DM_PCI_COMPAT */
/**
* dm_pciauto_config_device() - configure a device ready for use
*
* Space is allocated for each PCI base address register (BAR) so that the
* devices are mapped into memory and I/O space ready for use.
*
* @dev: Device to configure
* Return: 0 if OK, -ve on error
*/
int dm_pciauto_config_device(struct udevice *dev);
/**
* pci_conv_32_to_size() - convert a 32-bit read value to the given size
*
* Some PCI buses must always perform 32-bit reads. The data must then be
* shifted and masked to reflect the required access size and offset. This
* function performs this transformation.
*
* @value: Value to transform (32-bit value read from @offset & ~3)
* @offset: Register offset that was read
* @size: Required size of the result
* Return: the value that would have been obtained if the read had been
* performed at the given offset with the correct size
*/
ulong pci_conv_32_to_size(ulong value, uint offset, enum pci_size_t size);
/**
* pci_conv_size_to_32() - update a 32-bit value to prepare for a write
*
* Some PCI buses must always perform 32-bit writes. To emulate a smaller
* write the old 32-bit data must be read, updated with the required new data
* and written back as a 32-bit value. This function performs the
* transformation from the old value to the new value.
*
* @value: Value to transform (32-bit value read from @offset & ~3)
* @offset: Register offset that should be written
* @size: Required size of the write
* Return: the value that should be written as a 32-bit access to @offset & ~3.
*/
ulong pci_conv_size_to_32(ulong old, ulong value, uint offset,
enum pci_size_t size);
/**
* pci_get_controller() - obtain the controller to use for a bus
*
* @dev: Device to check
* Return: pointer to the controller device for this bus
*/
struct udevice *pci_get_controller(struct udevice *dev);
/**
* pci_get_regions() - obtain pointers to all the region types
*
* @dev: Device to check
* @iop: Returns a pointer to the I/O region, or NULL if none
* @memp: Returns a pointer to the memory region, or NULL if none
* @prefp: Returns a pointer to the pre-fetch region, or NULL if none
* Return: the number of non-NULL regions returned, normally 3
*/
int pci_get_regions(struct udevice *dev, struct pci_region **iop,
struct pci_region **memp, struct pci_region **prefp);
int
pci_get_dma_regions(struct udevice *dev, struct pci_region *memp, int index);
/**
* dm_pci_write_bar32() - Write the address of a BAR
*
* This writes a raw address to a bar
*
* @dev: PCI device to update
* @barnum: BAR number (0-5)
* @addr: BAR address
*/
void dm_pci_write_bar32(struct udevice *dev, int barnum, u32 addr);
/**
* dm_pci_read_bar32() - read a base address register from a device
*
* @dev: Device to check
* @barnum: Bar number to read (numbered from 0)
* @return: value of BAR
*/
u32 dm_pci_read_bar32(const struct udevice *dev, int barnum);
/**
* dm_pci_bus_to_phys() - convert a PCI bus address to a physical address
*
* @dev: Device containing the PCI address
* @addr: PCI address to convert
* @flags: Flags for the region type (PCI_REGION_...)
* Return: physical address corresponding to that PCI bus address
*/
phys_addr_t dm_pci_bus_to_phys(struct udevice *dev, pci_addr_t addr,
unsigned long flags);
/**
* dm_pci_phys_to_bus() - convert a physical address to a PCI bus address
*
* @dev: Device containing the bus address
* @addr: Physical address to convert
* @flags: Flags for the region type (PCI_REGION_...)
* Return: PCI bus address corresponding to that physical address
*/
pci_addr_t dm_pci_phys_to_bus(struct udevice *dev, phys_addr_t addr,
unsigned long flags);
/**
* dm_pci_map_bar() - get a virtual address associated with a BAR region
*
* Looks up a base address register and finds the physical memory address
* that corresponds to it.
* Can be used for 32b BARs 0-5 on type 0 functions and for 32b BARs 0-1 on
* type 1 functions.
* Can also be used on type 0 functions that support Enhanced Allocation for
* 32b/64b BARs. Note that duplicate BEI entries are not supported.
*
* @dev: Device to check
* @bar: Bar register offset (PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_...)
* @flags: Flags for the region type (PCI_REGION_...)
* @return: pointer to the virtual address to use or 0 on error
*/
void *dm_pci_map_bar(struct udevice *dev, int bar, int flags);
/**
* dm_pci_find_next_capability() - find a capability starting from an offset
*
* Tell if a device supports a given PCI capability. Returns the
* address of the requested capability structure within the device's
* PCI configuration space or 0 in case the device does not support it.
*
* Possible values for @cap:
*
* %PCI_CAP_ID_MSI Message Signalled Interrupts
* %PCI_CAP_ID_PCIX PCI-X
* %PCI_CAP_ID_EXP PCI Express
* %PCI_CAP_ID_MSIX MSI-X
*
* See PCI_CAP_ID_xxx for the complete capability ID codes.
*
* @dev: PCI device to query
* @start: offset to start from
* @cap: capability code
* @return: capability address or 0 if not supported
*/
int dm_pci_find_next_capability(struct udevice *dev, u8 start, int cap);
/**
* dm_pci_find_capability() - find a capability
*
* Tell if a device supports a given PCI capability. Returns the
* address of the requested capability structure within the device's
* PCI configuration space or 0 in case the device does not support it.
*
* Possible values for @cap:
*
* %PCI_CAP_ID_MSI Message Signalled Interrupts
* %PCI_CAP_ID_PCIX PCI-X
* %PCI_CAP_ID_EXP PCI Express
* %PCI_CAP_ID_MSIX MSI-X
*
* See PCI_CAP_ID_xxx for the complete capability ID codes.
*
* @dev: PCI device to query
* @cap: capability code
* @return: capability address or 0 if not supported
*/
int dm_pci_find_capability(struct udevice *dev, int cap);
/**
* dm_pci_find_next_ext_capability() - find an extended capability
* starting from an offset
*
* Tell if a device supports a given PCI express extended capability.
* Returns the address of the requested extended capability structure
* within the device's PCI configuration space or 0 in case the device
* does not support it.
*
* Possible values for @cap:
*
* %PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_ERR Advanced Error Reporting
* %PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_VC Virtual Channel
* %PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_DSN Device Serial Number
* %PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_PWR Power Budgeting
*
* See PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_xxx for the complete extended capability ID codes.
*
* @dev: PCI device to query
* @start: offset to start from
* @cap: extended capability code
* @return: extended capability address or 0 if not supported
*/
int dm_pci_find_next_ext_capability(struct udevice *dev, int start, int cap);
/**
* dm_pci_find_ext_capability() - find an extended capability
*
* Tell if a device supports a given PCI express extended capability.
* Returns the address of the requested extended capability structure
* within the device's PCI configuration space or 0 in case the device
* does not support it.
*
* Possible values for @cap:
*
* %PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_ERR Advanced Error Reporting
* %PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_VC Virtual Channel
* %PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_DSN Device Serial Number
* %PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_PWR Power Budgeting
*
* See PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_xxx for the complete extended capability ID codes.
*
* @dev: PCI device to query
* @cap: extended capability code
* @return: extended capability address or 0 if not supported
*/
int dm_pci_find_ext_capability(struct udevice *dev, int cap);
/**
* dm_pci_flr() - Perform FLR if the device suppoorts it
*
* @dev: PCI device to reset
* @return: 0 if OK, -ENOENT if FLR is not supported by dev
*/
int dm_pci_flr(struct udevice *dev);
#define dm_pci_virt_to_bus(dev, addr, flags) \
dm_pci_phys_to_bus(dev, (virt_to_phys(addr)), (flags))
#define dm_pci_bus_to_virt(dev, addr, flags, len, map_flags) \
map_physmem(dm_pci_bus_to_phys(dev, (addr), (flags)), \
(len), (map_flags))
#define dm_pci_phys_to_mem(dev, addr) \
dm_pci_phys_to_bus((dev), (addr), PCI_REGION_MEM)
#define dm_pci_mem_to_phys(dev, addr) \
dm_pci_bus_to_phys((dev), (addr), PCI_REGION_MEM)
#define dm_pci_phys_to_io(dev, addr) \
dm_pci_phys_to_bus((dev), (addr), PCI_REGION_IO)
#define dm_pci_io_to_phys(dev, addr) \
dm_pci_bus_to_phys((dev), (addr), PCI_REGION_IO)
#define dm_pci_virt_to_mem(dev, addr) \
dm_pci_virt_to_bus((dev), (addr), PCI_REGION_MEM)
#define dm_pci_mem_to_virt(dev, addr, len, map_flags) \
dm_pci_bus_to_virt((dev), (addr), PCI_REGION_MEM, (len), (map_flags))
#define dm_pci_virt_to_io(dev, addr) \
dm_pci_virt_to_bus((dev), (addr), PCI_REGION_IO)
#define dm_pci_io_to_virt(dev, addr, len, map_flags) \
dm_pci_bus_to_virt((dev), (addr), PCI_REGION_IO, (len), (map_flags))
/**
* dm_pci_find_device() - find a device by vendor/device ID
*
* @vendor: Vendor ID
* @device: Device ID
* @index: 0 to find the first match, 1 for second, etc.
* @devp: Returns pointer to the device, if found
* Return: 0 if found, -ve on error
*/
int dm_pci_find_device(unsigned int vendor, unsigned int device, int index,
struct udevice **devp);
/**
* dm_pci_find_class() - find a device by class
*
* @find_class: 3-byte (24-bit) class value to find
* @index: 0 to find the first match, 1 for second, etc.
* @devp: Returns pointer to the device, if found
* Return: 0 if found, -ve on error
*/
int dm_pci_find_class(uint find_class, int index, struct udevice **devp);
/**
* struct pci_emul_uc_priv - holds info about an emulator device
*
* There is always at most one emulator per client
*
* @client: Client device if any, else NULL
*/
struct pci_emul_uc_priv {
struct udevice *client;
};
/**
* struct dm_pci_emul_ops - PCI device emulator operations
*/
struct dm_pci_emul_ops {
/**
* read_config() - Read a PCI configuration value
*
* @dev: Emulated device to read from
* @offset: Byte offset within the device's configuration space
* @valuep: Place to put the returned value
* @size: Access size
* @return 0 if OK, -ve on error
*/
int (*read_config)(const struct udevice *dev, uint offset,
ulong *valuep, enum pci_size_t size);
/**
* write_config() - Write a PCI configuration value
*
* @dev: Emulated device to write to
* @offset: Byte offset within the device's configuration space
* @value: Value to write
* @size: Access size
* @return 0 if OK, -ve on error
*/
int (*write_config)(struct udevice *dev, uint offset, ulong value,
enum pci_size_t size);
/**
* read_io() - Read a PCI I/O value
*
* @dev: Emulated device to read from
* @addr: I/O address to read
* @valuep: Place to put the returned value
* @size: Access size
* @return 0 if OK, -ENOENT if @addr is not mapped by this device,
* other -ve value on error
*/
int (*read_io)(struct udevice *dev, unsigned int addr, ulong *valuep,
enum pci_size_t size);
/**
* write_io() - Write a PCI I/O value
*
* @dev: Emulated device to write from
* @addr: I/O address to write
* @value: Value to write
* @size: Access size
* @return 0 if OK, -ENOENT if @addr is not mapped by this device,
* other -ve value on error
*/
int (*write_io)(struct udevice *dev, unsigned int addr,
ulong value, enum pci_size_t size);
/**
* map_physmem() - Map a device into sandbox memory
*
* @dev: Emulated device to map
* @addr: Memory address, normally corresponding to a PCI BAR.
* The device should have been configured to have a BAR
* at this address.
* @lenp: On entry, the size of the area to map, On exit it is
* updated to the size actually mapped, which may be less
* if the device has less space
* @ptrp: Returns a pointer to the mapped address. The device's
* space can be accessed as @lenp bytes starting here
* @return 0 if OK, -ENOENT if @addr is not mapped by this device,
* other -ve value on error
*/
int (*map_physmem)(struct udevice *dev, phys_addr_t addr,
unsigned long *lenp, void **ptrp);
/**
* unmap_physmem() - undo a memory mapping
*
* This must be called after map_physmem() to undo the mapping.
* Some devices can use this to check what has been written into
* their mapped memory and perform an operations they require on it.
* In this way, map/unmap can be used as a sort of handshake between
* the emulated device and its users.
*
* @dev: Emuated device to unmap
* @vaddr: Mapped memory address, as passed to map_physmem()
* @len: Size of area mapped, as returned by map_physmem()
* @return 0 if OK, -ve on error
*/
int (*unmap_physmem)(struct udevice *dev, const void *vaddr,
unsigned long len);
};
/* Get access to a PCI device emulator's operations */
#define pci_get_emul_ops(dev) ((struct dm_pci_emul_ops *)(dev)->driver->ops)
/**
* sandbox_pci_get_emul() - Get the emulation device for a PCI device
*
* Searches for a suitable emulator for the given PCI bus device
*
* @bus: PCI bus to search
* @find_devfn: PCI device and function address (PCI_DEVFN())
* @containerp: Returns container device if found
* @emulp: Returns emulated device if found
* Return: 0 if found, -ENODEV if not found
*/
int sandbox_pci_get_emul(const struct udevice *bus, pci_dev_t find_devfn,
struct udevice **containerp, struct udevice **emulp);
/**
* sandbox_pci_get_client() - Find the client for an emulation device
*
* @emul: Emulation device to check
* @devp: Returns the client device emulated by this device
* Return: 0 if OK, -ENOENT if the device has no client yet
*/
int sandbox_pci_get_client(struct udevice *emul, struct udevice **devp);
/**
* board_pci_fixup_dev() - Board callback for PCI device fixups
*
* @bus: PCI bus
* @dev: PCI device
*/
extern void board_pci_fixup_dev(struct udevice *bus, struct udevice *dev);
/**
* PCI_DEVICE - macro used to describe a specific pci device
* @vend: the 16 bit PCI Vendor ID
* @dev: the 16 bit PCI Device ID
*
* This macro is used to create a struct pci_device_id that matches a
* specific device. The subvendor and subdevice fields will be set to
* PCI_ANY_ID.
*/
#define PCI_DEVICE(vend, dev) \
.vendor = (vend), .device = (dev), \
.subvendor = PCI_ANY_ID, .subdevice = PCI_ANY_ID
/**
* PCI_DEVICE_SUB - macro used to describe a specific pci device with subsystem
* @vend: the 16 bit PCI Vendor ID
* @dev: the 16 bit PCI Device ID
* @subvend: the 16 bit PCI Subvendor ID
* @subdev: the 16 bit PCI Subdevice ID
*
* This macro is used to create a struct pci_device_id that matches a
* specific device with subsystem information.
*/
#define PCI_DEVICE_SUB(vend, dev, subvend, subdev) \
.vendor = (vend), .device = (dev), \
.subvendor = (subvend), .subdevice = (subdev)
/**
* PCI_DEVICE_CLASS - macro used to describe a specific pci device class
* @dev_class: the class, subclass, prog-if triple for this device
* @dev_class_mask: the class mask for this device
*
* This macro is used to create a struct pci_device_id that matches a
* specific PCI class. The vendor, device, subvendor, and subdevice
* fields will be set to PCI_ANY_ID.
*/
#define PCI_DEVICE_CLASS(dev_class, dev_class_mask) \
.class = (dev_class), .class_mask = (dev_class_mask), \
.vendor = PCI_ANY_ID, .device = PCI_ANY_ID, \
.subvendor = PCI_ANY_ID, .subdevice = PCI_ANY_ID
/**
* PCI_VDEVICE - macro used to describe a specific pci device in short form
* @vend: the vendor name
* @dev: the 16 bit PCI Device ID
*
* This macro is used to create a struct pci_device_id that matches a
* specific PCI device. The subvendor, and subdevice fields will be set
* to PCI_ANY_ID. The macro allows the next field to follow as the device
* private data.
*/
#define PCI_VDEVICE(vend, dev) \
.vendor = PCI_VENDOR_ID_##vend, .device = (dev), \
.subvendor = PCI_ANY_ID, .subdevice = PCI_ANY_ID, 0, 0
/**
* struct pci_driver_entry - Matches a driver to its pci_device_id list
* @driver: Driver to use
* @match: List of match records for this driver, terminated by {}
*/
struct pci_driver_entry {
struct driver *driver;
const struct pci_device_id *match;
};
#define U_BOOT_PCI_DEVICE(__name, __match) \
ll_entry_declare(struct pci_driver_entry, __name, pci_driver_entry) = {\
.driver = llsym(struct driver, __name, driver), \
.match = __match, \
}
#endif /* __ASSEMBLY__ */
#endif /* _PCI_H */
使用U_BOOT_DRIVER创建一个驱动
U_BOOT_DRIVER(rochchip_pci) = {
.name = "rochchip_pci",
.id = UCLASS_PCI,
.of_match = rochchip_pci_ids,
.ops = &pcie_ops,
.probe = rochchip_pci_probe,
};UCLASS是U-Boot中的一个概念,代表通用设备类。它是用于组织和管理设备驱动程序的一个抽象层级。UCLASS用于将具有相似功能或属性的设备驱动程序进行分类,以便更好地组织、管理和调度这些驱动程序。
U-Boot中的每个设备驱动程序都被分配到一个特定的UCLASS中。每个UCLASS由一个标识符和相关的操作函数组成,这些操作函数用于在U-Boot中进行设备初始化、设备访问和设备操作。
通过使用UCLASS,可以实现设备驱动程序的抽象和分离,使得在U-Boot中添加、删除或修改设备驱动程序更加容易和灵活。每个UCLASS都具有与之对应的设备树节点,通过设备树中的绑定,可以将设备节点与对应的UCLASS进行关联。
从UCLASS的角度来看,U-Boot中的设备可以被认为是一种抽象的逻辑概念,而实际的设备驱动程序则是用于实现这些设备的硬件操作和功能实现的具体代码。通过使用UCLASS,可以有效地管理和组织各种设备的驱动程序,并提供统一的接口和操作方式,使得U-Boot能够更好地支持不同类型的硬件设备。
驱动与设备匹配定义。
static const struct udevice_id rochchip_pci_ids[] = {
{.compatible = "rochchip,pcie"},
{}};在UCLASS_PCI中需要实现读写pci配置空间的两个函数。
static const struct dm_pci_ops pcie_ops = {
.read_config = pcie_rochchip_read_config,
.write_config = pcie_rochchip_write_config,
};首先看一些pcie_rochchip_read_config、pcie_rochchip_read_config读函数。
static int pcie_rochchip_read_config(const struct udevice *bus, pci_dev_t bdf,
uint offset, ulong *valuep, enum pci_size_t size)
{
if (!g_pcie_scan_enable)
{
return -1;
}
return pcie_soc_read_config(bus, bdf, offset, valuep, size);
}
int pcie_soc_read_config(const struct udevice *bus, pci_dev_t bdf,
uint offset, ulong *valuep, enum pci_size_t size)
{
/* 最终执行pci_generic_soc_conf_address函数 */
return pci_generic_mmap_read_config(bus, pci_generic_soc_conf_address,
bdf, offset, valuep, size);
}
static int pcie_rochchip_write_config(const struct udevice *bus, pci_dev_t bdf,
uint offset, ulong value, enum pci_size_t size)
{
if (!g_pcie_scan_enable)
{
return -1;
}
return pcie_soc_write_config(bus, bdf, offset, value, size);
}
int pcie_soc_write_config(const struct udevice *bus, pci_dev_t bdf,
uint offset, ulong value, enum pci_size_t size)
{
/* 最终执行pci_generic_soc_conf_address函数 */
return pci_generic_mmap_write_config(bus, pci_generic_soc_conf_address,
bdf, offset, value, size);
}
static int pci_generic_soc_conf_address(const struct udevice *bus, pci_dev_t bdf,
uint offset, void **paddress)
{
struct rk_pcie_dev *pcie = dev_get_priv(bus);
struct rk_pcie_bd *bd = &pcie->bd;
return pci_soc_conf_addr(bd, bdf, offset, paddress);
}
/* 最终的读写函数在这里 */
int pci_soc_conf_addr(const struct rk_pcie_bd *bd, pci_dev_t bdf, uint32_t offset, void **paddr)
{
u32 busdev = 0;
int type = 0;
/* 检查是否linkup,通过读写IP的寄存器来判断是否linkup */
if (!rochchip_pcie_is_link_up(bd)) {
return -1;
}
/* 在pci.h中定义#define PCI_BUS(d) (((d) >> 16) & 0xff),高16位为总线号 */
if (0 == PCI_BUS(bdf)) {
if (PCI_MASK_BUS(bdf) > 0) {
return -1;
}
*paddr = bd->dbi_base + offset;
return 0;
}
/* 根据总线号、设备号、func号找到对应的busdev */
busdev += PCI_BUS(bdf) << 24;
busdev += PCI_DEV(bdf) << 19;
busdev += PCI_FUNC(bdf) << 16;
*paddr = bd->cfg_base + offset;
/* 判断是否为普通的EP设备(TYPR0) */
if (PCI_BUS(bdf) == 1) {
type = PCIE_ATU_TYPE_CFG0;
} else {
type = PCIE_ATU_TYPE_CFG1;
}
dw_pcie_prog_outbound_atu(bd, PCIE_ATU_REGION_INDEX1,
type, (u64)bd->cfg_base,
busdev, bd->cfg_size);
return 0;
}再来看,重中之重的probe函数。
static int rochchip_pci_probe(struct udevice *dev)
{
int ret = 0;
memset(&hbpdev, 0, sizeof(hbpdev));
hbpdev.udev = dev;
hbpdev.bd.udev = dev;
dev->priv_ = &hbpdev;
/* pcie IP初始化 */
ret = rochchip_pcie_bd_init(&hbpdev.bd);
if (ret < 0)
{
pr_err("rochchip bd init failed !\n");
return ret;
}
printf("rochchip pcie probe success !\n");
return 0;
}接着看下rochchip_pcie_bd_init函数初始化了哪些功能。
int rochchip_pcie_bd_init(struct rk_pcie_bd *bd)
{
int ret = 0;
/* 解析设备树 */
ret = rochchip_of_probe(bd);
if(ret < 0) {
dev_err(bd->udev, "of probe failed !\n");
return ret;
}
/* 硬件初始化 */
ret = rochchip_hw_init(bd);
if(ret < 0) {
dev_err(bd->udev, "rochchip hw failed !\n");
return ret;
}
bd->rbar = (void *)(unsigned long)PCIE_BAR2_BASE;
printf("rbar: %lx\n", (unsigned long)bd->rbar);
return 0;
}解析设备树
这里暂时不关注,继续向下看。
static int rochchip_of_probe(struct rk_pcie_bd *bd)
{
int ret = 0;
const void *fdt = gd->fdt_blob;
int node = dev_of_offset(bd->udev);
struct fdt_resource res;
bd->dbi_base = devfdt_remap_addr_index(bd->udev, 0);
if (NULL == bd->dbi_base) {
return -ENOMEM;
}
bd->dbi2_base = bd->dbi_base + ROCKCHIP_PCIE_DBI2_OFFSET;
ret = fdt_get_named_resource(fdt, node, "reg", "reg-names", "config", &res);
if (ret) {
return -ENOMEM;
}
bd->cfg_base = map_physmem(res.start, fdt_resource_size(&res), MAP_NOCACHE);
if (NULL == bd->cfg_base) {
return -ENOMEM;
}
bd->cfg_size = fdt_resource_size(&res);
bd->apb_base = devfdt_remap_addr_index(bd->udev, 2);
if (NULL == bd->dbi_base) {
return -ENOMEM;
}
ret = rochchip_reset_init(bd);
if(ret < 0) {
return ret;
}
bd->ops = &rk_bd_ops;
ret = clkreq_gpio_init(bd);
if(ret < 0) {
return ret;
}
return 0;
}pcie硬件初始化
static int rochchip_hw_init(struct rk_pcie_bd *bd)
{
int ret = 0;
/* 继续关注这里 */
ret = rochchip_pcie_board_set(bd);
if(ret < 0) {
dev_err(bd->udev, "rochchip board set failed !\n");
return ret;
}
/* 根据版本号和iaut判断并赋值AUT的基地址 */
if (bd->version >= 0x480A || (!bd->version && dw_pcie_iatu_unroll_enabled(bd))) {
bd->iatu_unroll_enabled = true;
bd->atu_base = bd->dbi_base + DEFAULT_DBI_ATU_OFFSET;
}
return 0;
}继续看下rochchip_pcie_board_set函数。
static int rochchip_pcie_board_set(struct rk_pcie_bd *bd)
{
int ret = 0;
/* 调用reset_assert进行软复位 */
rochchip_reset(bd, PCIE_SOFT_PERST);
/* 后面详细介绍rochchip_pcie_dev_init */
ret = rochchip_pcie_dev_init(bd);
if(ret) {
return ret;
}
/* 打开访问pcie的配置空间 */
block_cfg_request(bd);
/* 链路训练 */
ret = rochchip_pcie_establish_link(bd);
if(!board_is_rc()) {
/* 如果不是RC */
ep_hw_init(bd, 1);
}
/* 阻止访问pcie的配置空间 */
unblock_cfg_request(bd);
/* 通过操作IP的PCIE_DBI_RO_WR_EN寄存器,禁止写入 dbi 只读寄存器 */
dw_pcie_dbi_ro_wr_dis(bd);
/* 启动RC */
dw_pcie_setup_rc(bd);
return ret;
}1. rochchip_pcie_dev_init
static int32_t rochchip_pcie_dev_init(struct rk_pcie_bd *bd)
{
u32 val;
u16 val16;
if (aux_clk_init(bd) != 0) {
return -1;
}
if (phy_clk_init(bd) != 0) {
return -1;
}
/* 通过配置APB_CTL0寄存器的第24bit配置RC or !RC */
rochchip_pcie_mode_set(bd);
/* 通过读取IP的寄存器来判断是否linkup */
if (rochchip_pcie_is_link_up(bd) == 0) {
/* if link is down, need hold phy rst for DBI access */
val = apb_readl(bd, APB_CTL0);
val |= APB_CTL0_APP_HOLD_PHY_RST; /* app hold phy rst reset */
apb_writel(bd, APB_CTL0, val);
}
pr_info("PCI_EXP_LNKSTA %08x\n", dbi_readw(bd, ROCKCHIP_PCIE_CAPS_EXP_OFFSET + PCI_EXP_LNKSTA));
/* 通过配置PCIE_MISC_CONTROL_1_OFF寄存器,允许写入 dbi 只读寄存器 */
dw_pcie_dbi_ro_wr_en(bd);
/* 下面单独拿出来看 */
dw_pcie_setup(bd);
pr_info("PCI_EXP_LNKSTA %08x\n", dbi_readw(bd, ROCKCHIP_PCIE_CAPS_EXP_OFFSET + PCI_EXP_LNKSTA));
/* set MPS to 256 */
val16 =dbi_readw(bd, ROCKCHIP_PCIE_CAPS_EXP_OFFSET + PCI_EXP_DEVCTL);
val16 &= ~(u16)PCI_EXP_DEVCTL_PAYLOAD;
val16 |= 1 << 5;
dbi_writew(bd, ROCKCHIP_PCIE_CAPS_EXP_OFFSET + PCI_EXP_DEVCTL, val16);
return 0;
}
static void dw_pcie_setup(struct rk_pcie_bd *bd)
{
u32 val = 0;
if (bd->version >= 0x480A || (!bd->version && dw_pcie_iatu_unroll_enabled(bd))) {
bd->iatu_unroll_enabled = true;
bd->atu_base = bd->dbi_base + DEFAULT_DBI_ATU_OFFSET;
}
val = dbi_readl(bd, PCIE_PORT_LINK_CONTROL);
val &= ~PORT_LINK_FAST_LINK_MODE;
val |= PORT_LINK_DLL_LINK_EN;
dbi_writel(bd, PCIE_PORT_LINK_CONTROL, val);
/* set the number of lanes */
val &= ~PORT_LINK_FAST_LINK_MODE;
val &= ~PORT_LINK_MODE_MASK;
val |= PORT_LINK_MODE_2_LANES;
dbi_writel(bd, PCIE_PORT_LINK_CONTROL, val);
/* set link width speed control register */
val = dbi_readl(bd, PCIE_LINK_WIDTH_SPEED_CONTROL);
val &= ~PORT_LOGIC_LINK_WIDTH_MASK;
val |= PORT_LOGIC_LINK_WIDTH_2_LANES;
dbi_writel(bd, PCIE_LINK_WIDTH_SPEED_CONTROL, val);
}在PCI Express(PCIe)规范中,MPS代表Maximum Payload Size(最大有效载荷大小)。MPS用于指定PCIe传输中的有效载荷(payload)的最大数据大小。
有效载荷是指在PCIe传输中实际携带数据的部分,不包括控制和其他协议开销。有效载荷大小是通过MPS来定义的,它决定了每个PCIe事务中可携带的最大数据量。
PCIe设备的MPS值是通过链路训练和协商过程中的链路能力寄存器来确定的。设备和主机之间会交换链路能力寄存器的信息,包括各自支持的MPS值。然后双方会选择一个最小的MPS值作为链路的MPS值,以确保一致性。
MPS的值可以是128字节、256字节、512字节、1024字节、2048字节等,具体取决于设备和主机支持的MPS范围。
选择适当的MPS值对于PCIe性能至关重要。较小的MPS值可能会导致传输开销增加,因为每个事务都需要额外的控制开销。而较大的MPS值可以提高传输效率,尤其是对于大批量数据传输。因此,在PCIe系统中,合理选择MPS值能够在性能和效率方面实现平衡。
2. rochchip_pcie_establish_link
int32_t rochchip_pcie_establish_link(struct rk_pcie_bd *bd)
{
u32 val;
val = apb_readl(bd, APB_CTL0);
val &= ~APB_CTL0_APP_LTSSM_ENABLE; /* disable ltssm */
val |= APB_CTL0_APP_HOLD_PHY_RST; /* app hold phy rst reset */
apb_writel(bd, APB_CTL0, val);
rochchip_pcie_equalization(bd);
rochchip_reset(bd, PCIE_SOFT_PHY_RESET);
/* enable ltssm */
val = apb_readl(bd, APB_CTL0);
val |= APB_CTL0_APP_LTSSM_ENABLE;
val &= ~APB_CTL0_APP_HOLD_PHY_RST;
apb_writel(bd, APB_CTL0, val);
/* wait link up */
val = 1;
do {
if (rochchip_pcie_is_link_up(bd)) {
//pr_info("link up!\n");
printf("link up! val=%d\n", val);
return 0;
}
mdelay(val);
val = val * 2;
} while (val < PCIE_LTSSM_TIMEOUT);
pr_err("link up failed\n");
rk_pcie_show_regs(bd);
return -1;
}
static void rochchip_pcie_equalization(const struct rk_pcie_bd *bd)
{
u32 val = 0;
/* perform EQ. from databook A.3,允许写入 dbi 只读寄存器*/
dw_pcie_dbi_ro_wr_en(bd);
/* 配置GEN3寄存器 */
val = dbi_readl(bd, PCIE_GEN3_RELATED_OFF);
dev_dbg(bd->udev, "GEN3_RELATED_OFF %x\n", val);
val &= PCIE_GEN3_EQ_RXEQ_RGRDLESS_RXTS;
dbi_writel(bd, PCIE_GEN3_RELATED_OFF, val);
val = dbi_readl(bd, PCIE_GEN3_EQ_CTRL_OFF);
dev_dbg(bd->udev, "GEN3_EQ_CONTROL_OFF %x\n", val);
val &= (u32)PCIE_GEN3_EQ_DC_MODE;
val &= ~((u32)PCIE_GEN3_EQ_PRESET_ALL);
val |= (u32)PCIE_GEN3_EQ_PRESET_2_5; /* preset 2 & 5 */
val |= (u32)PCIE_GEN3_EQ_FOM_INC_INITIAL_EVAL;
dbi_writel(bd, PCIE_GEN3_EQ_CTRL_OFF, val);
val = dbi_readl(bd, PCIE_GEN3_EQ_FB_MODE_DIR_CHANGE_OFF);
dev_dbg(bd->udev, "GEN3_EQ_FB_MODE_DIR_CHANGE_OFF %x\n", val);
val &= (u32)PCIE_GEN3_EQ_FMDC_T_MIN_PHASE23;
val |= (u32)PCIE_GEN3_EQ_FMDC_T_MIN_PHASE23_10MS;
val &= (u32)PCIE_GEN3_EQ_FMDC_N_EVAL;
val |= (u32)PCIE_GEN3_EQ_FMDC_N_EVAL_3;
val &= (u32)PCIE_GEN3_EQ_FMDC_MAX_PRE_CUSROR_DELTA;
val |= (u32)PCIE_GEN3_EQ_FMDC_MAX_PRE_CUSROR_DELTA_1;
val &= (u32)PCIE_GEN3_EQ_FMDC_MAX_POST_CUSROR_DELTA;
val |= (u32)PCIE_GEN3_EQ_FMDC_MAX_POST_CUSROR_DELTA_1;
dbi_writel(bd, PCIE_GEN3_EQ_FB_MODE_DIR_CHANGE_OFF, val);
/* 关闭写入 dbi 只读寄存器 */
dw_pcie_dbi_ro_wr_dis(bd);
}在PCI Express(PCIe)规范中,LTSSM是指Link Training and Status State Machine(链路训练和状态状态机)。LTSSM是一种硬件状态机,用于管理PCIe链路的建立、配置和维护。
LTSSM负责PCIe链路的各个操作和状态转换,确保链路的正确建立、正确配置和正确操作。它控制PCIe链路中的信号传输、时序和通信协议,并管理链路的状态变化。
LTSSM通过一系列的状态进行链路的训练、协商和维护,以确保链路能够正常工作。主要的LTSSM状态包括: 1. Detect:检测链路的存在和初始化域。 2. Polling:对链路进行初始化,并确定链路速度和位宽。 3. Configuration:配置链路中的各个端点的协商参数。 4. Recovery:处理链路上的错误和异常情况,并尝试将链路恢复到正常工作状态。 5. Performance:在链路被配置和建立后,维持链路的性能和稳定状态。
LTSSM状态机的具体状态转换和行为是在PCIe规范中定义的,不同的PCIe设备和主机必须遵循这些规范来实现LTSSM状态机的行为。通过LTSSM,PCIe链路能够在正确的步骤和条件下建立并保持正常的通信和数据传输。
3. 如果非RC配置EP
static int ep_hw_init(struct rk_pcie_bd *bd, int probe)
{
/* EP初始化完成? */
dw_pcie_ep_init_complete(bd);
dw_pcie_ep_write_header(bd, 0, &rochchip_epf_header);
/* EP的bar空间配置 */
ep_bar_config(bd);
if (!probe) {
dev_command_recovery(bd);
bar_addr_recovery(bd);
}
unblock_cfg_request(bd);
return 0;
}
int dw_pcie_ep_init_complete(struct rk_pcie_bd *bd)
{
unsigned int offset;
unsigned int nbars;
u8 hdr_type;
u32 reg;
int i;
hdr_type = dbi_readb(bd, PCI_HEADER_TYPE) &
PCI_HEADER_TYPE_MASK;
if (hdr_type != PCI_HEADER_TYPE_NORMAL) {
printf("PCIe controller is not set to EP mode (hdr_type:0x%x)!\n", hdr_type);
return -1;
}
/* 让 ep 找到 PCIE 扩展帽位置 */
offset = dw_pcie_ep_find_ext_capability(bd, PCI_EXT_CAP_ID_REBAR);
dw_pcie_dbi_ro_wr_en(bd);
if (offset) {
reg = dbi_readl(bd, offset + PCI_REBAR_CTRL);
nbars = (reg & PCI_REBAR_CTRL_NBAR_MASK) >>
PCI_REBAR_CTRL_NBAR_SHIFT;
for (i = 0; i < nbars; i++, offset += PCI_REBAR_CTRL)
dbi_writel(bd, offset + PCI_REBAR_CAP, 0x0);
}
/* 上面已经详细介绍过了,PCIE 设置,如通道数、链路速度 */
dw_pcie_setup(bd);
dw_pcie_dbi_ro_wr_dis(bd);
return 0;
}
/* pcie ep config space header,这里主要配置了EP的配置空间的头部寄存器字段。 */
static int dw_pcie_ep_write_header(const struct rk_pcie_bd *bd, u8 func_no,
struct pci_epf_header *hdr)
{
unsigned int func_offset = 0;
dw_pcie_dbi_ro_wr_en(bd);
/* 配置vendor ID */
dbi_writew(bd, func_offset + PCI_VENDOR_ID, hdr->vendorid);
/* 配置device ID */
dbi_writew(bd, func_offset + PCI_DEVICE_ID, hdr->deviceid);
/* 配置reversion ID */
dbi_writeb(bd, func_offset + PCI_REVISION_ID, hdr->revid);
/* PCI_CLASS_PROG是Programming Interface字段,用于描述设备所支持的特定编程接口。 */
dbi_writeb(bd, func_offset + PCI_CLASS_PROG, hdr->progif_code);
/* PCI_CLASS_DEVICE是Device字段,用于描述设备的类别。 */
dbi_writew(bd, func_offset + PCI_CLASS_DEVICE,
hdr->subclass_code | hdr->baseclass_code << 8);
/* 配置line cache的大小 */
dbi_writeb(bd, func_offset + PCI_CACHE_LINE_SIZE,
hdr->cache_line_size);
/* PCI_SUBSYSTEM_VENDOR_ID(子系统供应商ID)和PCI_SUBSYSTEM_ID(子系统ID):这两个字段位于configuration Header的字节44和46处,用于表示PCI设备所属的子系统。它们通常用于唯一标识设备所在的整个系统或子系统。 */
dbi_writew(bd, func_offset + PCI_SUBSYSTEM_VENDOR_ID,
hdr->subsys_vendor_id);
dbi_writew(bd, func_offset + PCI_SUBSYSTEM_ID, hdr->subsys_id);
/* PCI_INTERRUPT_PIN(中断引脚):该字段位于Configuration Header的字节61处,指示设备使用的中断引脚。它表示设备提供中断信号的物理引脚的位置和编号。该字段的取值为0-4,分别表示不使用中断、使用INTA#、INTB#、INTC#和INTD#中断引脚 */
dbi_writeb(bd, func_offset + PCI_INTERRUPT_PIN,
hdr->interrupt_pin);
dw_pcie_dbi_ro_wr_dis(bd);
return 0;
}在PCI(Peripheral Component Interconnect)和PCI Express(PCIe)系统中,Class Code是一种用于标识和分类设备的编码方式。
Class Code是PCI设备的配置空间中的一个寄存器字段,用于描述设备的类别和特征。它由三个字段组成:Class、Subclass和Programming Interface。
Class字段:代表设备的高级类别。它提供了最广泛的设备分类,例如存储器控制器、显示控制器、网络控制器、桥接器等。
Subclass字段:在具体的设备类别下,Subclass字段提供了更详细的子类别信息。例如,在Class字段为存储器控制器的情况下,Subclass字段可以表示缓存控制器、RAID控制器等。
Programming Interface字段:在特定的设备子类别下,Programming Interface字段提供了更进一步的特定功能或配置接口的信息。
Class Code的取值是一种标准化的编码方式,需要遵循PCI和PCIe规范的定义。通过读取Class Code字段的值,软件可以识别和分类PCI设备,确定设备的功能和特性,并选择适当的驱动程序、配置和操作。
需要注意的是,Class Code字段的解释和支持取决于PCI和PCIe规范以及设备制造商的实现。因此,不同的设备和系统可能会支持不同的Class Code值和对应的功能集合。为了正确地处理PCI设备,软件需要根据具体的规范和文档理解和识别Class Code的含义和操作方式。
4. 配置RC
static void dw_pcie_setup_rc(struct rk_pcie_bd *bd)
{
u32 val = 0;
if (!board_is_rc()) {
return;
}
dw_pcie_dbi_ro_wr_en(bd);
dw_pcie_setup(bd);
///< setup RC BARs
dbi_writel(bd, PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_0, 0x00000004);
dbi_writel(bd, PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_1, 0x00000000);
/* Setup interrupt pins */
val = dbi_readl(bd, PCI_INTERRUPT_LINE);
val &= 0xffff00ff;
val |= 0x00000100;
dbi_writel(bd, PCI_INTERRUPT_LINE, val);
/* Setup bus numbers */
val = dbi_readl(bd, PCI_PRIMARY_BUS);
val &= 0xff000000;
val |= 0x00ff0100;
dbi_writel(bd, PCI_PRIMARY_BUS, val);
/* Setup command register */
val = dbi_readl(bd, PCI_COMMAND);
val &= 0xffff0000;
val |= PCI_COMMAND_IO | PCI_COMMAND_MEMORY |
PCI_COMMAND_MASTER | PCI_COMMAND_SERR;
dbi_writel(bd, PCI_COMMAND, val);
dbi_writel(bd, PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_0, 0);
dbi_writew(bd, PCI_CLASS_DEVICE, PCI_CLASS_BRIDGE_PCI);
val = dbi_readl(bd, PCIE_LINK_WIDTH_SPEED_CONTROL);
val |= PORT_LOGIC_SPEED_CHANGE;
dbi_writel(bd, PCIE_LINK_WIDTH_SPEED_CONTROL, val);
dw_pcie_dbi_ro_wr_dis(bd);
}三、kernel
host
 常规平台设备驱动。
常规平台设备驱动。
static const struct dev_pm_ops rockchip_pcie_pm_ops = {
NOIRQ_SYSTEM_SLEEP_PM_OPS(rockchip_pcie_suspend_noirq,
rockchip_pcie_resume_noirq)
};
static const struct of_device_id rockchip_pcie_of_match[] = {
{ .compatible = "rockchip,rk3399-pcie", },
{}
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of, rockchip_pcie_of_match);
static struct platform_driver rockchip_pcie_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "rockchip-pcie",
.of_match_table = rockchip_pcie_of_match,
.pm = &rockchip_pcie_pm_ops,
},
.probe = rockchip_pcie_probe,
.remove = rockchip_pcie_remove,
};
module_platform_driver(rockchip_pcie_driver);接着重点看一下probe函数。
static int rockchip_pcie_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct rockchip_pcie *rockchip;
struct device *dev = &pdev->dev;
struct pci_host_bridge *bridge;
int err;
if (!dev->of_node)
return -ENODEV;
/* Linux内核中的一个函数,用于在设备树中注册PCI(Peripheral Component Interconnect)主机桥 */
bridge = devm_pci_alloc_host_bridge(dev, sizeof(*rockchip));
if (!bridge)
return -ENOMEM;
/* 设置私有数据 */
rockchip = pci_host_bridge_priv(bridge);
platform_set_drvdata(pdev, rockchip);
rockchip->dev = dev;
rockchip->is_rc = true;
/* 解析设备树,这里没什么关注的 */
err = rockchip_pcie_parse_host_dt(rockchip);
if (err)
return err;
/* 使能相关时钟 */
err = rockchip_pcie_enable_clocks(rockchip);
if (err)
return err;
/* 配置vpci,这里只是根据电压配置,调用regulator_enable配置。 */
err = rockchip_pcie_set_vpcie(rockchip);
if (err) {
dev_err(dev, "failed to set vpcie regulator\n");
goto err_set_vpcie;
}
/* 初始化port,重点分析 */
err = rockchip_pcie_host_init_port(rockchip);
if (err)
goto err_vpcie;
/* 调用irq_domain_add_linear()函数会将中断域与指定的中断控制器关联起来,并对中断号进行线性分配。通过调用这个函数,可以在系统中添加一个新的中断域,并将其与给定的中断控制器相关联。 */
err = rockchip_pcie_init_irq_domain(rockchip);
if (err < 0)
goto err_deinit_port;
/* 配置ATU,重点分析 */
err = rockchip_pcie_cfg_atu(rockchip);
if (err)
goto err_remove_irq_domain;
rockchip->msg_region = devm_ioremap(dev, rockchip->msg_bus_addr, SZ_1M);
if (!rockchip->msg_region) {
err = -ENOMEM;
goto err_remove_irq_domain;
}
bridge->sysdata = rockchip;
/* 这里面配置的读写配置空间的操作函数 */
bridge->ops = &rockchip_pcie_ops;
/* 配置中断处理函数,重点分析 */
err = rockchip_pcie_setup_irq(rockchip);
if (err)
goto err_remove_irq_domain;
/* 这里面配置了PCIE_CORE_INT_MASK和LCS的寄存器。"LCS" 是 "Link Control Speed" 的缩写 */
rockchip_pcie_enable_interrupts(rockchip);
err = pci_host_probe(bridge);
if (err < 0)
goto err_remove_irq_domain;
return 0;
err_remove_irq_domain:
irq_domain_remove(rockchip->irq_domain);
err_deinit_port:
rockchip_pcie_deinit_phys(rockchip);
err_vpcie:
if (!IS_ERR(rockchip->vpcie12v))
regulator_disable(rockchip->vpcie12v);
if (!IS_ERR(rockchip->vpcie3v3))
regulator_disable(rockchip->vpcie3v3);
regulator_disable(rockchip->vpcie1v8);
regulator_disable(rockchip->vpcie0v9);
err_set_vpcie:
rockchip_pcie_disable_clocks(rockchip);
return err;
}1. rockchip_pcie_host_init_port
/**
* rockchip_pcie_host_init_port - Initialize hardware
* @rockchip: PCIe port information
*/
static int rockchip_pcie_host_init_port(struct rockchip_pcie *rockchip)
{
struct device *dev = rockchip->dev;
int err, i = MAX_LANE_NUM;
u32 status;
/* 拉低ep_gpio */
gpiod_set_value_cansleep(rockchip->ep_gpio, 0);
/* 这个函数单独拿出来 */
err = rockchip_pcie_init_port(rockchip);
if (err)
return err;
/* 这段代码的目的是修复通过调整已传输的帧超时值(FTS)计数以退出L0s状态。对于PCIe设备,L0s状态是一种低功耗链接状态,用于在设备之间降低功耗并提供低延迟的数据传输。 */
/* Fix the transmitted FTS count desired to exit from L0s. */
status = rockchip_pcie_read(rockchip, PCIE_CORE_CTRL_PLC1);
status = (status & ~PCIE_CORE_CTRL_PLC1_FTS_MASK) |
(PCIE_CORE_CTRL_PLC1_FTS_CNT << PCIE_CORE_CTRL_PLC1_FTS_SHIFT);
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, status, PCIE_CORE_CTRL_PLC1);
/*
* Set RC's captured slot power limit and scale if
* vpcie3v3 available. The default values are both zero
* which means the software should set these two according
* to the actual power supply.
*/
rockchip_pcie_set_power_limit(rockchip);
/* "LCS"代表"Link Control Speed",用于表示链路速度控制。 */
/* Set RC's clock architecture as common clock */
status = rockchip_pcie_read(rockchip, PCIE_RC_CONFIG_LCS);
status |= PCI_EXP_LNKSTA_SLC << 16;
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, status, PCIE_RC_CONFIG_LCS);
/* 目的是将RC(Root Complex,即PCIe控制器)的RCB(Receiver Buffer)设置为128。RCB(Receiver Buffer)是指PCIe(Peripheral Component Interconnect Express)中接收缓冲区。在PCIe链路上,接收缓冲区用于存储从传输层接收到的数据包。 */
/* Set RC's RCB to 128 */
status = rockchip_pcie_read(rockchip, PCIE_RC_CONFIG_LCS);
status |= PCI_EXP_LNKCTL_RCB;
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, status, PCIE_RC_CONFIG_LCS);
/* Enable Gen1 training,使能gen1的链路训练 */
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, PCIE_CLIENT_LINK_TRAIN_ENABLE,
PCIE_CLIENT_CONFIG);
/* 拉高ep_gpio,TODO:疑问,这里拉低又拉高为甚? */
gpiod_set_value_cansleep(rockchip->ep_gpio, 1);
/* 500ms timeout value should be enough for Gen1/2 training */
err = readl_poll_timeout(rockchip->apb_base + PCIE_CLIENT_BASIC_STATUS1,
status, PCIE_LINK_UP(status), 20,
500 * USEC_PER_MSEC);
if (err) {
dev_err(dev, "PCIe link training gen1 timeout!\n");
goto err_power_off_phy;
}
if (rockchip->link_gen == 2) {
/*
* Enable retrain for gen2. This should be configured only after
* gen1 finished.
*/
status = rockchip_pcie_read(rockchip, PCIE_RC_CONFIG_LCS);
status |= PCI_EXP_LNKCTL_RL;
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, status, PCIE_RC_CONFIG_LCS);
err = readl_poll_timeout(rockchip->apb_base + PCIE_CORE_CTRL,
status, PCIE_LINK_IS_GEN2(status), 20,
500 * USEC_PER_MSEC);
if (err)
dev_dbg(dev, "PCIe link training gen2 timeout, fall back to gen1!\n");
}
/* Check the final link width from negotiated lane counter from MGMT */
status = rockchip_pcie_read(rockchip, PCIE_CORE_CTRL);
status = 0x1 << ((status & PCIE_CORE_PL_CONF_LANE_MASK) >>
PCIE_CORE_PL_CONF_LANE_SHIFT);
dev_dbg(dev, "current link width is x%d\n", status);
/* Power off unused lane(s) */
rockchip->lanes_map = rockchip_pcie_lane_map(rockchip);
for (i = 0; i < MAX_LANE_NUM; i++) {
if (!(rockchip->lanes_map & BIT(i))) {
dev_dbg(dev, "idling lane %d\n", i);
phy_power_off(rockchip->phys[i]);
}
}
/* 配置vendor ID */
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, ROCKCHIP_VENDOR_ID,
PCIE_CORE_CONFIG_VENDOR);
/* PCIE_RC_CONFIG_RID_CCR是PCIe控制器的配置寄存器,用于设置和控制PCIe控制器的资源ID计数(RID)和可配置消息控制寄存器(Configuration Cycle Receiver,CCR)。 */
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip,
PCI_CLASS_BRIDGE_PCI_NORMAL << 8,
PCIE_RC_CONFIG_RID_CCR);
/* THP(TLP Processing Hints)是PCIe(Peripheral Component Interconnect Express)协议中定义的一种能力,用于在PCIe设备之间指示和优化数据传输。
以下是PCIe中常见的低功耗状态和链接状态:
L0:即正常工作状态,设备处于活动状态,进行数据传输和处理。
L0s:这是一种较低功耗的状态,适用于设备处于空闲或轻负载状态时。在L0s状态下,设备可以进入低功耗模式,以节省能量,但仍然能及时响应来自根复杂性控制器的传输请求。
L1.1、L1.2和L1.3:这些是L1子状态的不同版本。L1子状态是一种更低功耗的状态,允许设备在非活动状态下降低链接层的功耗。不同版本的L1子状态提供了不同程度的功耗优化和功能增强。
L2:这是一种更深的睡眠状态,用于进一步降低设备的功耗。在L2状态下,设备可以完全停止链接层和传输层的活动,并处于较低的功耗状态,但在退入/唤醒时需要相对较长的时间。
这些低功耗状态和链接状态通过链路训练和协商的过程来进行协商和切换。具体设备支持的状态以及如何进入和退出这些状态,取决于设备的硬件能力、驱动程序的支持和链路层协商的结果。
通过使用这些低功耗状态,PCIe设备可以根据负载需求和空闲时间来优化功耗和能效,从而提高系统的性能和节能性。
*/
/* Clear THP cap's next cap pointer to remove L1 substate cap */
status = rockchip_pcie_read(rockchip, PCIE_RC_CONFIG_THP_CAP);
status &= ~PCIE_RC_CONFIG_THP_CAP_NEXT_MASK;
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, status, PCIE_RC_CONFIG_THP_CAP);
/* Clear L0s from RC's link cap */
if (of_property_read_bool(dev->of_node, "aspm-no-l0s")) {
status = rockchip_pcie_read(rockchip, PCIE_RC_CONFIG_LINK_CAP);
status &= ~PCIE_RC_CONFIG_LINK_CAP_L0S;
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, status, PCIE_RC_CONFIG_LINK_CAP);
}
/* 修改PCIe RC(Root Complex)的DCSR(Device Control and Status Register)配置寄存器,以更新最大有效负载大小(MPS - Maximum Payload Size)的设置。 */
status = rockchip_pcie_read(rockchip, PCIE_RC_CONFIG_DCSR);
status &= ~PCIE_RC_CONFIG_DCSR_MPS_MASK;
status |= PCIE_RC_CONFIG_DCSR_MPS_256;
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, status, PCIE_RC_CONFIG_DCSR);
return 0;
err_power_off_phy:
while (i--)
phy_power_off(rockchip->phys[i]);
i = MAX_LANE_NUM;
while (i--)
phy_exit(rockchip->phys[i]);
return err;
}rockchip_pcie_init_port
int rockchip_pcie_init_port(struct rockchip_pcie *rockchip)
{
struct device *dev = rockchip->dev;
int err, i;
u32 regs;
err = reset_control_assert(rockchip->aclk_rst);
if (err) {
dev_err(dev, "assert aclk_rst err %d\n", err);
return err;
}
err = reset_control_assert(rockchip->pclk_rst);
if (err) {
dev_err(dev, "assert pclk_rst err %d\n", err);
return err;
}
err = reset_control_assert(rockchip->pm_rst);
if (err) {
dev_err(dev, "assert pm_rst err %d\n", err);
return err;
}
for (i = 0; i < MAX_LANE_NUM; i++) {
err = phy_init(rockchip->phys[i]);
if (err) {
dev_err(dev, "init phy%d err %d\n", i, err);
goto err_exit_phy;
}
}
err = reset_control_assert(rockchip->core_rst);
if (err) {
dev_err(dev, "assert core_rst err %d\n", err);
goto err_exit_phy;
}
err = reset_control_assert(rockchip->mgmt_rst);
if (err) {
dev_err(dev, "assert mgmt_rst err %d\n", err);
goto err_exit_phy;
}
err = reset_control_assert(rockchip->mgmt_sticky_rst);
if (err) {
dev_err(dev, "assert mgmt_sticky_rst err %d\n", err);
goto err_exit_phy;
}
err = reset_control_assert(rockchip->pipe_rst);
if (err) {
dev_err(dev, "assert pipe_rst err %d\n", err);
goto err_exit_phy;
}
udelay(10);
err = reset_control_deassert(rockchip->pm_rst);
if (err) {
dev_err(dev, "deassert pm_rst err %d\n", err);
goto err_exit_phy;
}
err = reset_control_deassert(rockchip->aclk_rst);
if (err) {
dev_err(dev, "deassert aclk_rst err %d\n", err);
goto err_exit_phy;
}
err = reset_control_deassert(rockchip->pclk_rst);
if (err) {
dev_err(dev, "deassert pclk_rst err %d\n", err);
goto err_exit_phy;
}
/* 配置GEN的版本 */
if (rockchip->link_gen == 2)
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, PCIE_CLIENT_GEN_SEL_2,
PCIE_CLIENT_CONFIG);
else
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, PCIE_CLIENT_GEN_SEL_1,
PCIE_CLIENT_CONFIG);
/*
链路训练(TRAIN):
链路训练是PCIe设备在链接建立过程中进行的一系列协商和校准步骤。通过链路训练,PCIe设备可以确定稳定的链接状态,并在数据传输之前进行必要的优化和适配。
链路训练包括各种协议消息的交换,用于校准传输参数,例如电流调整、时钟和延迟校准、速度协商等。链路训练的过程是自动的,由PCIe设备和根复杂性控制器(Root Complex)之间的交互来完成。
ARI(Address Range Identifier):
ARI是一种扩展的PCIe寻址机制,用于支持更高的设备编号和更大的设备数量。传统的PCIe寻址机制使用8位的总线编号(Bus Number)、5位的设备号(Device Number)和3位的函数号(Function Number)来唯一标识一个设备。
而ARI机制则使用16位的总线编号、12位的设备号和3位的函数号,从而支持更多的设备编号。使用ARI寻址机制时,需要相应的支持和配置。ARI机制提供了更高的可扩展性,可以支持更大规模的PCIe系统,尤其在多个根端点(Root Endpoint)的系统中。
lane的数量
*/
regs = PCIE_CLIENT_LINK_TRAIN_ENABLE | PCIE_CLIENT_ARI_ENABLE |
PCIE_CLIENT_CONF_LANE_NUM(rockchip->lanes);
if (rockchip->is_rc)
regs |= PCIE_CLIENT_CONF_ENABLE | PCIE_CLIENT_MODE_RC;
else
regs |= PCIE_CLIENT_CONF_DISABLE | PCIE_CLIENT_MODE_EP;
/* 配置模式和能力 */
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, regs, PCIE_CLIENT_CONFIG);
for (i = 0; i < MAX_LANE_NUM; i++) {
err = phy_power_on(rockchip->phys[i]);
if (err) {
dev_err(dev, "power on phy%d err %d\n", i, err);
goto err_power_off_phy;
}
}
/*
* Please don't reorder the deassert sequence of the following
* four reset pins.
*/
err = reset_control_deassert(rockchip->mgmt_sticky_rst);
if (err) {
dev_err(dev, "deassert mgmt_sticky_rst err %d\n", err);
goto err_power_off_phy;
}
err = reset_control_deassert(rockchip->core_rst);
if (err) {
dev_err(dev, "deassert core_rst err %d\n", err);
goto err_power_off_phy;
}
err = reset_control_deassert(rockchip->mgmt_rst);
if (err) {
dev_err(dev, "deassert mgmt_rst err %d\n", err);
goto err_power_off_phy;
}
err = reset_control_deassert(rockchip->pipe_rst);
if (err) {
dev_err(dev, "deassert pipe_rst err %d\n", err);
goto err_power_off_phy;
}
return 0;
err_power_off_phy:
while (i--)
phy_power_off(rockchip->phys[i]);
i = MAX_LANE_NUM;
err_exit_phy:
while (i--)
phy_exit(rockchip->phys[i]);
return err;
}2. rockchip_pcie_cfg_atu
PCIe中的ATU(Address Translation Unit)是用于地址转换的模块或单元。ATU负责在PCIe系统中进行地址映射和重定向,使得PCIe设备能够正确访问和传输数据。
ATU主要负责以下功能:
地址转换:ATU将PCIe设备发出的事务层数据包(TLP - Transaction Layer Packet)的地址从设备本地地址(DMA地址)转换为系统物理地址。这样,PCIe设备可以使用主机系统的物理地址空间,而不需要直接访问和管理系统的物理地址。
地址重定向:ATU还可以根据系统配置,对某些特定的地址范围进行地址重定向。例如,将某个特定设备的地址范围映射到系统中的另一个设备或内存区域。这可以实现内存映射IO(Memory-Mapped IO)的功能,使得设备可以像访问内存一样直接访问其他设备的寄存器或数据。
通过ATU的地址转换和重定向功能,PCIe设备可以实现与主机系统的无缝交互和数据传输。它简化了设备驱动程序的设计,使得设备在不同系统上的移植和兼容性更加容易。
static int rockchip_pcie_cfg_atu(struct rockchip_pcie *rockchip)
{
struct device *dev = rockchip->dev;
struct pci_host_bridge *bridge = pci_host_bridge_from_priv(rockchip);
struct resource_entry *entry;
u64 pci_addr, size;
int offset;
int err;
int reg_no;
/* 下面补充展示,TODO:疑问配置BAR0? */
rockchip_pcie_cfg_configuration_accesses(rockchip,
AXI_WRAPPER_TYPE0_CFG);
entry = resource_list_first_type(&bridge->windows, IORESOURCE_MEM);
if (!entry)
return -ENODEV;
size = resource_size(entry->res);
pci_addr = entry->res->start - entry->offset;
rockchip->msg_bus_addr = pci_addr;
for (reg_no = 0; reg_no < (size >> 20); reg_no++) {
/* 配置outbound,建立mem映射 */
err = rockchip_pcie_prog_ob_atu(rockchip, reg_no + 1,
AXI_WRAPPER_MEM_WRITE,
20 - 1,
pci_addr + (reg_no << 20),
0);
if (err) {
dev_err(dev, "program RC mem outbound ATU failed\n");
return err;
}
}
err = rockchip_pcie_prog_ib_atu(rockchip, 2, 32 - 1, 0x0, 0);
if (err) {
dev_err(dev, "program RC mem inbound ATU failed\n");
return err;
}
entry = resource_list_first_type(&bridge->windows, IORESOURCE_IO);
if (!entry)
return -ENODEV;
/* store the register number offset to program RC io outbound ATU */
offset = size >> 20;
size = resource_size(entry->res);
pci_addr = entry->res->start - entry->offset;
/* 配inbound,建io映射 */
for (reg_no = 0; reg_no < (size >> 20); reg_no++) {
err = rockchip_pcie_prog_ob_atu(rockchip,
reg_no + 1 + offset,
AXI_WRAPPER_IO_WRITE,
20 - 1,
pci_addr + (reg_no << 20),
0);
if (err) {
dev_err(dev, "program RC io outbound ATU failed\n");
return err;
}
}
/* assign message regions */
rockchip_pcie_prog_ob_atu(rockchip, reg_no + 1 + offset,
AXI_WRAPPER_NOR_MSG,
20 - 1, 0, 0);
rockchip->msg_bus_addr += ((reg_no + offset) << 20);
return err;
}
void rockchip_pcie_cfg_configuration_accesses(
struct rockchip_pcie *rockchip, u32 type)
{
u32 ob_desc_0;
/* Configuration Accesses for region 0 */
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, 0x0, PCIE_RC_BAR_CONF);
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip,
(RC_REGION_0_ADDR_TRANS_L + RC_REGION_0_PASS_BITS),
PCIE_CORE_OB_REGION_ADDR0);
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, RC_REGION_0_ADDR_TRANS_H,
PCIE_CORE_OB_REGION_ADDR1);
ob_desc_0 = rockchip_pcie_read(rockchip, PCIE_CORE_OB_REGION_DESC0);
ob_desc_0 &= ~(RC_REGION_0_TYPE_MASK);
ob_desc_0 |= (type | (0x1 << 23));
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, ob_desc_0, PCIE_CORE_OB_REGION_DESC0);
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, 0x0, PCIE_CORE_OB_REGION_DESC1);
}
static int rockchip_pcie_prog_ob_atu(struct rockchip_pcie *rockchip,
int region_no, int type, u8 num_pass_bits,
u32 lower_addr, u32 upper_addr)
{
u32 ob_addr_0;
u32 ob_addr_1;
u32 ob_desc_0;
u32 aw_offset;
if (region_no >= MAX_AXI_WRAPPER_REGION_NUM)
return -EINVAL;
if (num_pass_bits + 1 < 8)
return -EINVAL;
if (num_pass_bits > 63)
return -EINVAL;
if (region_no == 0) {
if (AXI_REGION_0_SIZE < (2ULL << num_pass_bits))
return -EINVAL;
}
if (region_no != 0) {
if (AXI_REGION_SIZE < (2ULL << num_pass_bits))
return -EINVAL;
}
aw_offset = (region_no << OB_REG_SIZE_SHIFT);
ob_addr_0 = num_pass_bits & PCIE_CORE_OB_REGION_ADDR0_NUM_BITS;
ob_addr_0 |= lower_addr & PCIE_CORE_OB_REGION_ADDR0_LO_ADDR;
ob_addr_1 = upper_addr;
ob_desc_0 = (1 << 23 | type);
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, ob_addr_0,
PCIE_CORE_OB_REGION_ADDR0 + aw_offset);
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, ob_addr_1,
PCIE_CORE_OB_REGION_ADDR1 + aw_offset);
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, ob_desc_0,
PCIE_CORE_OB_REGION_DESC0 + aw_offset);
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, 0,
PCIE_CORE_OB_REGION_DESC1 + aw_offset);
return 0;
}
3. rockchip_pcie_setup_irq
static int rockchip_pcie_setup_irq(struct rockchip_pcie *rockchip)
{
int irq, err;
struct device *dev = rockchip->dev;
struct platform_device *pdev = to_platform_device(dev);
irq = platform_get_irq_byname(pdev, "sys");
if (irq < 0)
return irq;
err = devm_request_irq(dev, irq, rockchip_pcie_subsys_irq_handler,
IRQF_SHARED, "pcie-sys", rockchip);
if (err) {
dev_err(dev, "failed to request PCIe subsystem IRQ\n");
return err;
}
irq = platform_get_irq_byname(pdev, "legacy");
if (irq < 0)
return irq;
irq_set_chained_handler_and_data(irq,
rockchip_pcie_legacy_int_handler,
rockchip);
irq = platform_get_irq_byname(pdev, "client");
if (irq < 0)
return irq;
err = devm_request_irq(dev, irq, rockchip_pcie_client_irq_handler,
IRQF_SHARED, "pcie-client", rockchip);
if (err) {
dev_err(dev, "failed to request PCIe client IRQ\n");
return err;
}
return 0;
}
static irqreturn_t rockchip_pcie_subsys_irq_handler(int irq, void *arg)
{
struct rockchip_pcie *rockchip = arg;
struct device *dev = rockchip->dev;
u32 reg;
u32 sub_reg;
reg = rockchip_pcie_read(rockchip, PCIE_CLIENT_INT_STATUS);
if (reg & PCIE_CLIENT_INT_LOCAL) {
dev_dbg(dev, "local interrupt received\n");
sub_reg = rockchip_pcie_read(rockchip, PCIE_CORE_INT_STATUS);
if (sub_reg & PCIE_CORE_INT_PRFPE)
dev_dbg(dev, "parity error detected while reading from the PNP receive FIFO RAM\n");
if (sub_reg & PCIE_CORE_INT_CRFPE)
dev_dbg(dev, "parity error detected while reading from the Completion Receive FIFO RAM\n");
if (sub_reg & PCIE_CORE_INT_RRPE)
dev_dbg(dev, "parity error detected while reading from replay buffer RAM\n");
if (sub_reg & PCIE_CORE_INT_PRFO)
dev_dbg(dev, "overflow occurred in the PNP receive FIFO\n");
if (sub_reg & PCIE_CORE_INT_CRFO)
dev_dbg(dev, "overflow occurred in the completion receive FIFO\n");
if (sub_reg & PCIE_CORE_INT_RT)
dev_dbg(dev, "replay timer timed out\n");
if (sub_reg & PCIE_CORE_INT_RTR)
dev_dbg(dev, "replay timer rolled over after 4 transmissions of the same TLP\n");
if (sub_reg & PCIE_CORE_INT_PE)
dev_dbg(dev, "phy error detected on receive side\n");
if (sub_reg & PCIE_CORE_INT_MTR)
dev_dbg(dev, "malformed TLP received from the link\n");
if (sub_reg & PCIE_CORE_INT_UCR)
dev_dbg(dev, "malformed TLP received from the link\n");
if (sub_reg & PCIE_CORE_INT_FCE)
dev_dbg(dev, "an error was observed in the flow control advertisements from the other side\n");
if (sub_reg & PCIE_CORE_INT_CT)
dev_dbg(dev, "a request timed out waiting for completion\n");
if (sub_reg & PCIE_CORE_INT_UTC)
dev_dbg(dev, "unmapped TC error\n");
if (sub_reg & PCIE_CORE_INT_MMVC)
dev_dbg(dev, "MSI mask register changes\n");
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, sub_reg, PCIE_CORE_INT_STATUS);
} else if (reg & PCIE_CLIENT_INT_PHY) {
dev_dbg(dev, "phy link changes\n");
rockchip_pcie_update_txcredit_mui(rockchip);
rockchip_pcie_clr_bw_int(rockchip);
}
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, reg & PCIE_CLIENT_INT_LOCAL,
PCIE_CLIENT_INT_STATUS);
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
static irqreturn_t rockchip_pcie_client_irq_handler(int irq, void *arg)
{
struct rockchip_pcie *rockchip = arg;
struct device *dev = rockchip->dev;
u32 reg;
reg = rockchip_pcie_read(rockchip, PCIE_CLIENT_INT_STATUS);
if (reg & PCIE_CLIENT_INT_LEGACY_DONE)
dev_dbg(dev, "legacy done interrupt received\n");
if (reg & PCIE_CLIENT_INT_MSG)
dev_dbg(dev, "message done interrupt received\n");
if (reg & PCIE_CLIENT_INT_HOT_RST)
dev_dbg(dev, "hot reset interrupt received\n");
if (reg & PCIE_CLIENT_INT_DPA)
dev_dbg(dev, "dpa interrupt received\n");
if (reg & PCIE_CLIENT_INT_FATAL_ERR)
dev_dbg(dev, "fatal error interrupt received\n");
if (reg & PCIE_CLIENT_INT_NFATAL_ERR)
dev_dbg(dev, "no fatal error interrupt received\n");
if (reg & PCIE_CLIENT_INT_CORR_ERR)
dev_dbg(dev, "correctable error interrupt received\n");
if (reg & PCIE_CLIENT_INT_PHY)
dev_dbg(dev, "phy interrupt received\n");
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, reg & (PCIE_CLIENT_INT_LEGACY_DONE |
PCIE_CLIENT_INT_MSG | PCIE_CLIENT_INT_HOT_RST |
PCIE_CLIENT_INT_DPA | PCIE_CLIENT_INT_FATAL_ERR |
PCIE_CLIENT_INT_NFATAL_ERR |
PCIE_CLIENT_INT_CORR_ERR |
PCIE_CLIENT_INT_PHY),
PCIE_CLIENT_INT_STATUS);
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}4. pci_host_probe
 设备的扫描从
设备的扫描从pci_scan_root_bus_bridge开始,首先需要先向系统注册一个host bridge,在注册的过程中需要创建一个root bus,也就是bus 0,在pci_register_host_bridge函数中,主要是一系列的初始化和注册工作,此外还为总线分配资源,包括地址空间等;
pci_scan_child_bus开始,从bus 0向下扫描并添加设备,这个过程由pci_scan_child_bus_extend来完成;从
pci_scan_child_bus_extend的流程可以看出,主要有两大块:
PCI设备扫描,从循环也能看出来,每条总线支持32个设备,每个设备支持8个功能,扫描完设备后将设备注册进系统,pci_scan_device的过程中会去读取PCI设备的配置空间,获取到BAR的相关信息,细节不表了;
PCI桥设备扫描,PCI桥是用于连接上一级PCI总线和下一级PCI总线的,当发现有下一级总线时,创建子结构,并再次调用
pci_scan_child_bus_extend的函数来扫描下一级的总线,从这个过程看,就是一个递归过程。
从设备的扫描过程看,这是一个典型的DFS(
Depth First Search)过程,熟悉数据结构与算法的同学应该清楚,这就类似典型的走迷宫的过程;
如果你对上述的流程还不清楚,再来一张图:
图中的数字代表的就是扫描的过程,当遍历到PCI桥设备的时候,会一直穷究到底,然后再返回来;
当枚举过程结束后,系统中就已经维护了PCI设备的各类信息了,在设备驱动匹配模型中,总线和设备都已经具备了,剩下的就是写个驱动了。
EP
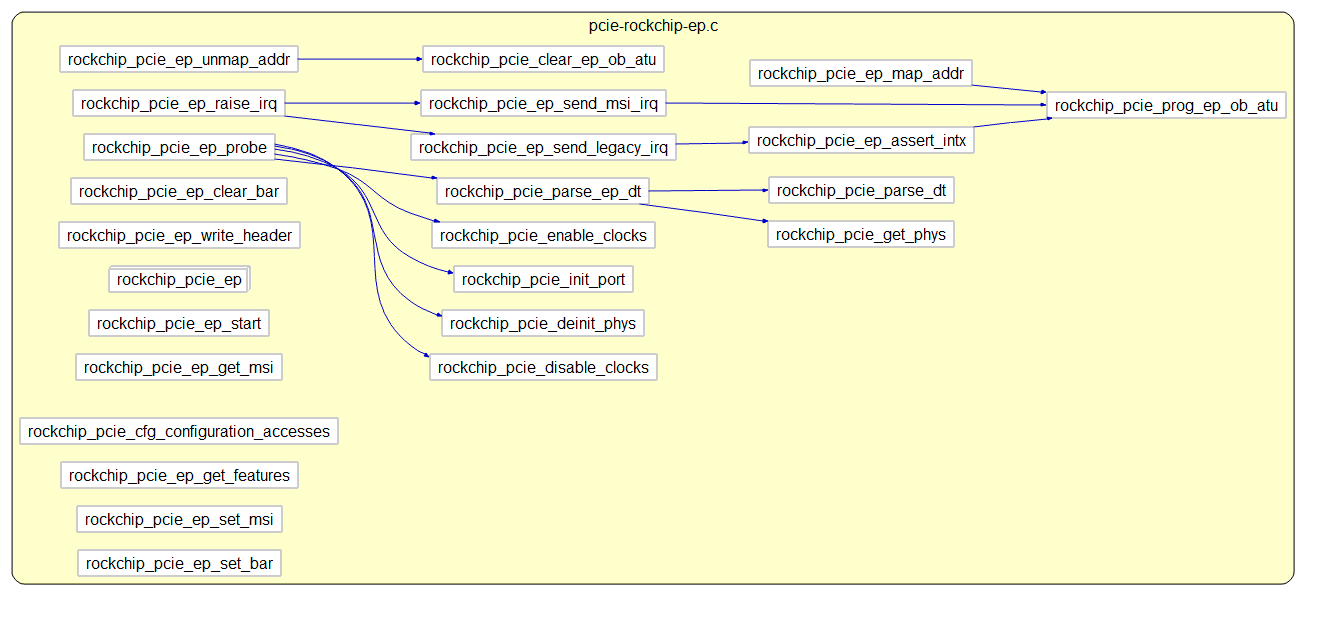 同样的是常规的平台设备驱动。
同样的是常规的平台设备驱动。
static const struct of_device_id rockchip_pcie_ep_of_match[] = {
{ .compatible = "rockchip,rk3399-pcie-ep"},
{},
};
static struct platform_driver rockchip_pcie_ep_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "rockchip-pcie-ep",
.of_match_table = rockchip_pcie_ep_of_match,
},
.probe = rockchip_pcie_ep_probe,
};
builtin_platform_driver(rockchip_pcie_ep_driver);中断关注下probe函数
static int rockchip_pcie_ep_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct device *dev = &pdev->dev;
struct rockchip_pcie_ep *ep;
struct rockchip_pcie *rockchip;
struct pci_epc *epc;
size_t max_regions;
int err;
ep = devm_kzalloc(dev, sizeof(*ep), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!ep)
return -ENOMEM;
rockchip = &ep->rockchip;
rockchip->is_rc = false;
rockchip->dev = dev;
/* 在Linux内核中创建PCIe EPC(Endpoint Configuration)设备的函数。PCIe EPC设备是一种虚拟设备,允许Linux内核通过PCIe总线与其他PCIe设备进行通信。OPS将在后面展开介绍 */
epc = devm_pci_epc_create(dev, &rockchip_pcie_epc_ops);
if (IS_ERR(epc)) {
dev_err(dev, "failed to create epc device\n");
return PTR_ERR(epc);
}
ep->epc = epc;
epc_set_drvdata(epc, ep);
/* 解析设备树,rockchip,max-outbound-regions","max-functions" */
err = rockchip_pcie_parse_ep_dt(rockchip, ep);
if (err)
return err;
/* 使能时钟 */
err = rockchip_pcie_enable_clocks(rockchip);
if (err)
return err;
/* 一些硬件配置,链路训练等,host部分有详细解析,不再赘述 */
err = rockchip_pcie_init_port(rockchip);
if (err)
goto err_disable_clocks;
/* Establish the link automatically,自动建立连接 */
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, PCIE_CLIENT_LINK_TRAIN_ENABLE,
PCIE_CLIENT_CONFIG);
max_regions = ep->max_regions;
ep->ob_addr = devm_kcalloc(dev, max_regions, sizeof(*ep->ob_addr),
GFP_KERNEL);
if (!ep->ob_addr) {
err = -ENOMEM;
goto err_uninit_port;
}
/* Only enable function 0 by default */
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, BIT(0), PCIE_CORE_PHY_FUNC_CFG);
err = pci_epc_mem_init(epc, rockchip->mem_res->start,
resource_size(rockchip->mem_res), PAGE_SIZE);
if (err < 0) {
dev_err(dev, "failed to initialize the memory space\n");
goto err_uninit_port;
}
ep->irq_cpu_addr = pci_epc_mem_alloc_addr(epc, &ep->irq_phys_addr,
SZ_128K);
if (!ep->irq_cpu_addr) {
dev_err(dev, "failed to reserve memory space for MSI\n");
err = -ENOMEM;
goto err_epc_mem_exit;
}
ep->irq_pci_addr = ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_DUMMY_IRQ_ADDR;
return 0;
err_epc_mem_exit:
pci_epc_mem_exit(epc);
err_uninit_port:
rockchip_pcie_deinit_phys(rockchip);
err_disable_clocks:
rockchip_pcie_disable_clocks(rockchip);
return err;
}1. rockchip_pcie_epc_ops
static const struct pci_epc_ops rockchip_pcie_epc_ops = {
.write_header = rockchip_pcie_ep_write_header,
.set_bar = rockchip_pcie_ep_set_bar,
.clear_bar = rockchip_pcie_ep_clear_bar,
.map_addr = rockchip_pcie_ep_map_addr,
.unmap_addr = rockchip_pcie_ep_unmap_addr,
.set_msi = rockchip_pcie_ep_set_msi,
.get_msi = rockchip_pcie_ep_get_msi,
.raise_irq = rockchip_pcie_ep_raise_irq,
.start = rockchip_pcie_ep_start,
.get_features = rockchip_pcie_ep_get_features,
};struct pci_epc_ops是一个用于定义PCIe EPC(Endpoint Configuration)设备操作函数的结构体。这个结构体中的成员函数用于配置和操作PCIe EPC设备,与EPC驱动程序之间的接口。
该结构体通常由EPC驱动程序的开发者定义,并在创建PCIe EPC设备时传递给相应的函数,以便内核在需要时调用这些函数。下面是struct pci_epc_ops结构体的一些常用的成员函数和用途:
setup: 用于初始化和配置PCIe EPC设备,例如配置PCIe EPC设备的寄存器、设置DMA传输等。add_device: 当有新的PCIe设备连接到EPC设备上时,调用此函数来通知EPC驱动程序有新设备连接,并进行相应的配置和处理。remove_device: 当一个PCIe设备从EPC设备上断开连接时,调用此函数来通知EPC驱动程序有设备断开,并进行相应的清理和处理。get_features: 获取PCIe EPC设备的功能特性,例如支持的最大的传输速度、最大的传输带宽等。set_features: 设置和配置PCIe EPC设备的功能特性,例如设置最大的传输速度、使能或禁用特定的功能等。get_msi: 获取MSI(Message Signaled Interrupt)配置信息,用于配置和管理PCIe设备的中断。set_msi: 配置PCIe设备的MSI,用于设置和控制设备的中断。get_msix: 获取MSIX(Message Signaled Interrupts eXtended)配置信息,类似于MSI但提供了更强大的中断处理能力。set_msix: 配置PCIe设备的MSIX,用于设置和控制设备的中断。get_bar: 获取PCIe EPC设备的BAR(Base Address Register)配置信息,包括BAR的基地址、大小和属性等。set_bar: 配置PCIe EPC设备的BAR,用于设置和控制BAR的基地址、大小和属性。
这些成员函数用于定义并实现与PCIe EPC设备相关的操作,使EPC驱动程序能够与内核和其他PCIe设备进行通信和交互。在使用struct pci_epc_ops时,驱动程序开发者需要根据具体硬件平台和要求来定义和实现相应的操作函数。
需要注意的是,具体PCIe EPC操作函数的实现和使用方式可能因不同的硬件平台和驱动程序而有所不同。在实际使用和开发中,请参考相关的硬件文档、设备树和驱动程序的文档,以了解如何正确定义和实现struct pci_epc_ops的成员函数。
1.1 write_header
static int rockchip_pcie_ep_write_header(struct pci_epc *epc, u8 fn, u8 vfn,
struct pci_epf_header *hdr)
{
struct rockchip_pcie_ep *ep = epc_get_drvdata(epc);
struct rockchip_pcie *rockchip = &ep->rockchip;
/* All functions share the same vendor ID with function 0 */
if (fn == 0) {
u32 vid_regs = (hdr->vendorid & GENMASK(15, 0)) |
(hdr->subsys_vendor_id & GENMASK(31, 16)) << 16;
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, vid_regs,
PCIE_CORE_CONFIG_VENDOR);
}
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, hdr->deviceid << 16,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_FUNC_BASE(fn) + PCI_VENDOR_ID);
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip,
hdr->revid |
hdr->progif_code << 8 |
hdr->subclass_code << 16 |
hdr->baseclass_code << 24,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_FUNC_BASE(fn) + PCI_REVISION_ID);
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, hdr->cache_line_size,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_FUNC_BASE(fn) +
PCI_CACHE_LINE_SIZE);
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, hdr->subsys_id << 16,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_FUNC_BASE(fn) +
PCI_SUBSYSTEM_VENDOR_ID);
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, hdr->interrupt_pin << 8,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_FUNC_BASE(fn) +
PCI_INTERRUPT_LINE);
return 0;
}1.2 set_bar
static int rockchip_pcie_ep_set_bar(struct pci_epc *epc, u8 fn, u8 vfn,
struct pci_epf_bar *epf_bar)
{
struct rockchip_pcie_ep *ep = epc_get_drvdata(epc);
struct rockchip_pcie *rockchip = &ep->rockchip;
dma_addr_t bar_phys = epf_bar->phys_addr;
enum pci_barno bar = epf_bar->barno;
int flags = epf_bar->flags;
u32 addr0, addr1, reg, cfg, b, aperture, ctrl;
u64 sz;
/* BAR size is 2^(aperture + 7) */
sz = max_t(size_t, epf_bar->size, MIN_EP_APERTURE);
/*
* roundup_pow_of_two() returns an unsigned long, which is not suited
* for 64bit values.
*/
sz = 1ULL << fls64(sz - 1);
aperture = ilog2(sz) - 7; /* 128B -> 0, 256B -> 1, 512B -> 2, ... */
if ((flags & PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_SPACE) == PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_SPACE_IO) {
ctrl = ROCKCHIP_PCIE_CORE_BAR_CFG_CTRL_IO_32BITS;
} else {
bool is_prefetch = !!(flags & PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_MEM_PREFETCH);
bool is_64bits = sz > SZ_2G;
if (is_64bits && (bar & 1))
return -EINVAL;
if (is_64bits && is_prefetch)
ctrl =
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_CORE_BAR_CFG_CTRL_PREFETCH_MEM_64BITS;
else if (is_prefetch)
ctrl =
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_CORE_BAR_CFG_CTRL_PREFETCH_MEM_32BITS;
else if (is_64bits)
ctrl = ROCKCHIP_PCIE_CORE_BAR_CFG_CTRL_MEM_64BITS;
else
ctrl = ROCKCHIP_PCIE_CORE_BAR_CFG_CTRL_MEM_32BITS;
}
if (bar < BAR_4) {
reg = ROCKCHIP_PCIE_CORE_EP_FUNC_BAR_CFG0(fn);
b = bar;
} else {
reg = ROCKCHIP_PCIE_CORE_EP_FUNC_BAR_CFG1(fn);
b = bar - BAR_4;
}
addr0 = lower_32_bits(bar_phys);
addr1 = upper_32_bits(bar_phys);
cfg = rockchip_pcie_read(rockchip, reg);
cfg &= ~(ROCKCHIP_PCIE_CORE_EP_FUNC_BAR_CFG_BAR_APERTURE_MASK(b) |
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_CORE_EP_FUNC_BAR_CFG_BAR_CTRL_MASK(b));
cfg |= (ROCKCHIP_PCIE_CORE_EP_FUNC_BAR_CFG_BAR_APERTURE(b, aperture) |
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_CORE_EP_FUNC_BAR_CFG_BAR_CTRL(b, ctrl));
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, cfg, reg);
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, addr0,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_AT_IB_EP_FUNC_BAR_ADDR0(fn, bar));
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, addr1,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_AT_IB_EP_FUNC_BAR_ADDR1(fn, bar));
return 0;
}1.3 clear_bar
static void rockchip_pcie_ep_clear_bar(struct pci_epc *epc, u8 fn, u8 vfn,
struct pci_epf_bar *epf_bar)
{
struct rockchip_pcie_ep *ep = epc_get_drvdata(epc);
struct rockchip_pcie *rockchip = &ep->rockchip;
u32 reg, cfg, b, ctrl;
enum pci_barno bar = epf_bar->barno;
if (bar < BAR_4) {
reg = ROCKCHIP_PCIE_CORE_EP_FUNC_BAR_CFG0(fn);
b = bar;
} else {
reg = ROCKCHIP_PCIE_CORE_EP_FUNC_BAR_CFG1(fn);
b = bar - BAR_4;
}
ctrl = ROCKCHIP_PCIE_CORE_BAR_CFG_CTRL_DISABLED;
cfg = rockchip_pcie_read(rockchip, reg);
cfg &= ~(ROCKCHIP_PCIE_CORE_EP_FUNC_BAR_CFG_BAR_APERTURE_MASK(b) |
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_CORE_EP_FUNC_BAR_CFG_BAR_CTRL_MASK(b));
cfg |= ROCKCHIP_PCIE_CORE_EP_FUNC_BAR_CFG_BAR_CTRL(b, ctrl);
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, cfg, reg);
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, 0x0,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_AT_IB_EP_FUNC_BAR_ADDR0(fn, bar));
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, 0x0,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_AT_IB_EP_FUNC_BAR_ADDR1(fn, bar));
}1.4 map_addr
static int rockchip_pcie_ep_map_addr(struct pci_epc *epc, u8 fn, u8 vfn,
phys_addr_t addr, u64 pci_addr,
size_t size)
{
struct rockchip_pcie_ep *ep = epc_get_drvdata(epc);
struct rockchip_pcie *pcie = &ep->rockchip;
u32 r;
r = find_first_zero_bit(&ep->ob_region_map, BITS_PER_LONG);
/*
* Region 0 is reserved for configuration space and shouldn't
* be used elsewhere per TRM, so leave it out.
*/
if (r >= ep->max_regions - 1) {
dev_err(&epc->dev, "no free outbound region\n");
return -EINVAL;
}
rockchip_pcie_prog_ep_ob_atu(pcie, fn, r, AXI_WRAPPER_MEM_WRITE, addr,
pci_addr, size);
set_bit(r, &ep->ob_region_map);
ep->ob_addr[r] = addr;
return 0;
}1.5 unmap_addr
static void rockchip_pcie_ep_unmap_addr(struct pci_epc *epc, u8 fn, u8 vfn,
phys_addr_t addr)
{
struct rockchip_pcie_ep *ep = epc_get_drvdata(epc);
struct rockchip_pcie *rockchip = &ep->rockchip;
u32 r;
for (r = 0; r < ep->max_regions - 1; r++)
if (ep->ob_addr[r] == addr)
break;
/*
* Region 0 is reserved for configuration space and shouldn't
* be used elsewhere per TRM, so leave it out.
*/
if (r == ep->max_regions - 1)
return;
rockchip_pcie_clear_ep_ob_atu(rockchip, r);
ep->ob_addr[r] = 0;
clear_bit(r, &ep->ob_region_map);
}1.6 set_msi
static int rockchip_pcie_ep_set_msi(struct pci_epc *epc, u8 fn, u8 vfn,
u8 multi_msg_cap)
{
struct rockchip_pcie_ep *ep = epc_get_drvdata(epc);
struct rockchip_pcie *rockchip = &ep->rockchip;
u16 flags;
flags = rockchip_pcie_read(rockchip,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_FUNC_BASE(fn) +
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_MSI_CTRL_REG);
flags &= ~ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_MSI_CTRL_MMC_MASK;
flags |=
((multi_msg_cap << 1) << ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_MSI_CTRL_MMC_OFFSET) |
PCI_MSI_FLAGS_64BIT;
flags &= ~ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_MSI_CTRL_MASK_MSI_CAP;
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, flags,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_FUNC_BASE(fn) +
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_MSI_CTRL_REG);
return 0;
}
1.7 get_msi
static int rockchip_pcie_ep_get_msi(struct pci_epc *epc, u8 fn, u8 vfn)
{
struct rockchip_pcie_ep *ep = epc_get_drvdata(epc);
struct rockchip_pcie *rockchip = &ep->rockchip;
u16 flags;
flags = rockchip_pcie_read(rockchip,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_FUNC_BASE(fn) +
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_MSI_CTRL_REG);
if (!(flags & ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_MSI_CTRL_ME))
return -EINVAL;
return ((flags & ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_MSI_CTRL_MME_MASK) >>
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_MSI_CTRL_MME_OFFSET);
}1.8 raise_irq
static int rockchip_pcie_ep_raise_irq(struct pci_epc *epc, u8 fn, u8 vfn,
enum pci_epc_irq_type type,
u16 interrupt_num)
{
struct rockchip_pcie_ep *ep = epc_get_drvdata(epc);
switch (type) {
case PCI_EPC_IRQ_LEGACY:
return rockchip_pcie_ep_send_legacy_irq(ep, fn, 0);
case PCI_EPC_IRQ_MSI:
return rockchip_pcie_ep_send_msi_irq(ep, fn, interrupt_num);
default:
return -EINVAL;
}
}
static int rockchip_pcie_ep_send_legacy_irq(struct rockchip_pcie_ep *ep, u8 fn,
u8 intx)
{
u16 cmd;
cmd = rockchip_pcie_read(&ep->rockchip,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_FUNC_BASE(fn) +
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_CMD_STATUS);
if (cmd & PCI_COMMAND_INTX_DISABLE)
return -EINVAL;
/*
* Should add some delay between toggling INTx per TRM vaguely saying
* it depends on some cycles of the AHB bus clock to function it. So
* add sufficient 1ms here.
*/
rockchip_pcie_ep_assert_intx(ep, fn, intx, true);
mdelay(1);
rockchip_pcie_ep_assert_intx(ep, fn, intx, false);
return 0;
}
static void rockchip_pcie_ep_assert_intx(struct rockchip_pcie_ep *ep, u8 fn,
u8 intx, bool is_asserted)
{
struct rockchip_pcie *rockchip = &ep->rockchip;
u32 r = ep->max_regions - 1;
u32 offset;
u32 status;
u8 msg_code;
if (unlikely(ep->irq_pci_addr != ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_PCI_LEGACY_IRQ_ADDR ||
ep->irq_pci_fn != fn)) {
rockchip_pcie_prog_ep_ob_atu(rockchip, fn, r,
AXI_WRAPPER_NOR_MSG,
ep->irq_phys_addr, 0, 0);
ep->irq_pci_addr = ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_PCI_LEGACY_IRQ_ADDR;
ep->irq_pci_fn = fn;
}
intx &= 3;
if (is_asserted) {
ep->irq_pending |= BIT(intx);
msg_code = ROCKCHIP_PCIE_MSG_CODE_ASSERT_INTA + intx;
} else {
ep->irq_pending &= ~BIT(intx);
msg_code = ROCKCHIP_PCIE_MSG_CODE_DEASSERT_INTA + intx;
}
status = rockchip_pcie_read(rockchip,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_FUNC_BASE(fn) +
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_CMD_STATUS);
status &= ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_CMD_STATUS_IS;
if ((status != 0) ^ (ep->irq_pending != 0)) {
status ^= ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_CMD_STATUS_IS;
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, status,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_FUNC_BASE(fn) +
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_CMD_STATUS);
}
offset =
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_MSG_ROUTING(ROCKCHIP_PCIE_MSG_ROUTING_LOCAL_INTX) |
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_MSG_CODE(msg_code) | ROCKCHIP_PCIE_MSG_NO_DATA;
writel(0, ep->irq_cpu_addr + offset);
}
static int rockchip_pcie_ep_send_msi_irq(struct rockchip_pcie_ep *ep, u8 fn,
u8 interrupt_num)
{
struct rockchip_pcie *rockchip = &ep->rockchip;
u16 flags, mme, data, data_mask;
u8 msi_count;
u64 pci_addr, pci_addr_mask = 0xff;
/* Check MSI enable bit */
flags = rockchip_pcie_read(&ep->rockchip,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_FUNC_BASE(fn) +
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_MSI_CTRL_REG);
if (!(flags & ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_MSI_CTRL_ME))
return -EINVAL;
/* Get MSI numbers from MME */
mme = ((flags & ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_MSI_CTRL_MME_MASK) >>
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_MSI_CTRL_MME_OFFSET);
msi_count = 1 << mme;
if (!interrupt_num || interrupt_num > msi_count)
return -EINVAL;
/* Set MSI private data */
data_mask = msi_count - 1;
data = rockchip_pcie_read(rockchip,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_FUNC_BASE(fn) +
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_MSI_CTRL_REG +
PCI_MSI_DATA_64);
data = (data & ~data_mask) | ((interrupt_num - 1) & data_mask);
/* Get MSI PCI address */
pci_addr = rockchip_pcie_read(rockchip,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_FUNC_BASE(fn) +
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_MSI_CTRL_REG +
PCI_MSI_ADDRESS_HI);
pci_addr <<= 32;
pci_addr |= rockchip_pcie_read(rockchip,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_FUNC_BASE(fn) +
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_EP_MSI_CTRL_REG +
PCI_MSI_ADDRESS_LO);
pci_addr &= GENMASK_ULL(63, 2);
/* Set the outbound region if needed. */
if (unlikely(ep->irq_pci_addr != (pci_addr & ~pci_addr_mask) ||
ep->irq_pci_fn != fn)) {
rockchip_pcie_prog_ep_ob_atu(rockchip, fn, ep->max_regions - 1,
AXI_WRAPPER_MEM_WRITE,
ep->irq_phys_addr,
pci_addr & ~pci_addr_mask,
pci_addr_mask + 1);
ep->irq_pci_addr = (pci_addr & ~pci_addr_mask);
ep->irq_pci_fn = fn;
}
writew(data, ep->irq_cpu_addr + (pci_addr & pci_addr_mask));
return 0;
}
static void rockchip_pcie_prog_ep_ob_atu(struct rockchip_pcie *rockchip, u8 fn,
u32 r, u32 type, u64 cpu_addr,
u64 pci_addr, size_t size)
{
u64 sz = 1ULL << fls64(size - 1);
int num_pass_bits = ilog2(sz);
u32 addr0, addr1, desc0, desc1;
bool is_nor_msg = (type == AXI_WRAPPER_NOR_MSG);
/* The minimal region size is 1MB */
if (num_pass_bits < 8)
num_pass_bits = 8;
cpu_addr -= rockchip->mem_res->start;
addr0 = ((is_nor_msg ? 0x10 : (num_pass_bits - 1)) &
PCIE_CORE_OB_REGION_ADDR0_NUM_BITS) |
(lower_32_bits(cpu_addr) & PCIE_CORE_OB_REGION_ADDR0_LO_ADDR);
addr1 = upper_32_bits(is_nor_msg ? cpu_addr : pci_addr);
desc0 = ROCKCHIP_PCIE_AT_OB_REGION_DESC0_DEVFN(fn) | type;
desc1 = 0;
if (is_nor_msg) {
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, 0,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_AT_OB_REGION_PCI_ADDR0(r));
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, 0,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_AT_OB_REGION_PCI_ADDR1(r));
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, desc0,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_AT_OB_REGION_DESC0(r));
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, desc1,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_AT_OB_REGION_DESC1(r));
} else {
/* PCI bus address region */
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, addr0,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_AT_OB_REGION_PCI_ADDR0(r));
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, addr1,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_AT_OB_REGION_PCI_ADDR1(r));
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, desc0,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_AT_OB_REGION_DESC0(r));
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, desc1,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_AT_OB_REGION_DESC1(r));
addr0 =
((num_pass_bits - 1) & PCIE_CORE_OB_REGION_ADDR0_NUM_BITS) |
(lower_32_bits(cpu_addr) &
PCIE_CORE_OB_REGION_ADDR0_LO_ADDR);
addr1 = upper_32_bits(cpu_addr);
}
/* CPU bus address region */
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, addr0,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_AT_OB_REGION_CPU_ADDR0(r));
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, addr1,
ROCKCHIP_PCIE_AT_OB_REGION_CPU_ADDR1(r));
}1.9 start
static int rockchip_pcie_ep_start(struct pci_epc *epc)
{
struct rockchip_pcie_ep *ep = epc_get_drvdata(epc);
struct rockchip_pcie *rockchip = &ep->rockchip;
struct pci_epf *epf;
u32 cfg;
cfg = BIT(0);
list_for_each_entry(epf, &epc->pci_epf, list)
cfg |= BIT(epf->func_no);
rockchip_pcie_write(rockchip, cfg, PCIE_CORE_PHY_FUNC_CFG);
return 0;
}1.10 get_features
static const struct pci_epc_features rockchip_pcie_epc_features = {
.linkup_notifier = false,
.msi_capable = true,
.msix_capable = false,
};
static const struct pci_epc_features*
rockchip_pcie_ep_get_features(struct pci_epc *epc, u8 func_no, u8 vfunc_no)
{
return &rockchip_pcie_epc_features;
}四、总结
这里只看到了soc厂商对IP驱动的实现和适配,还需要了解的事情:
对框架层的衔接;
工具的支持;
对协议的梳理。

